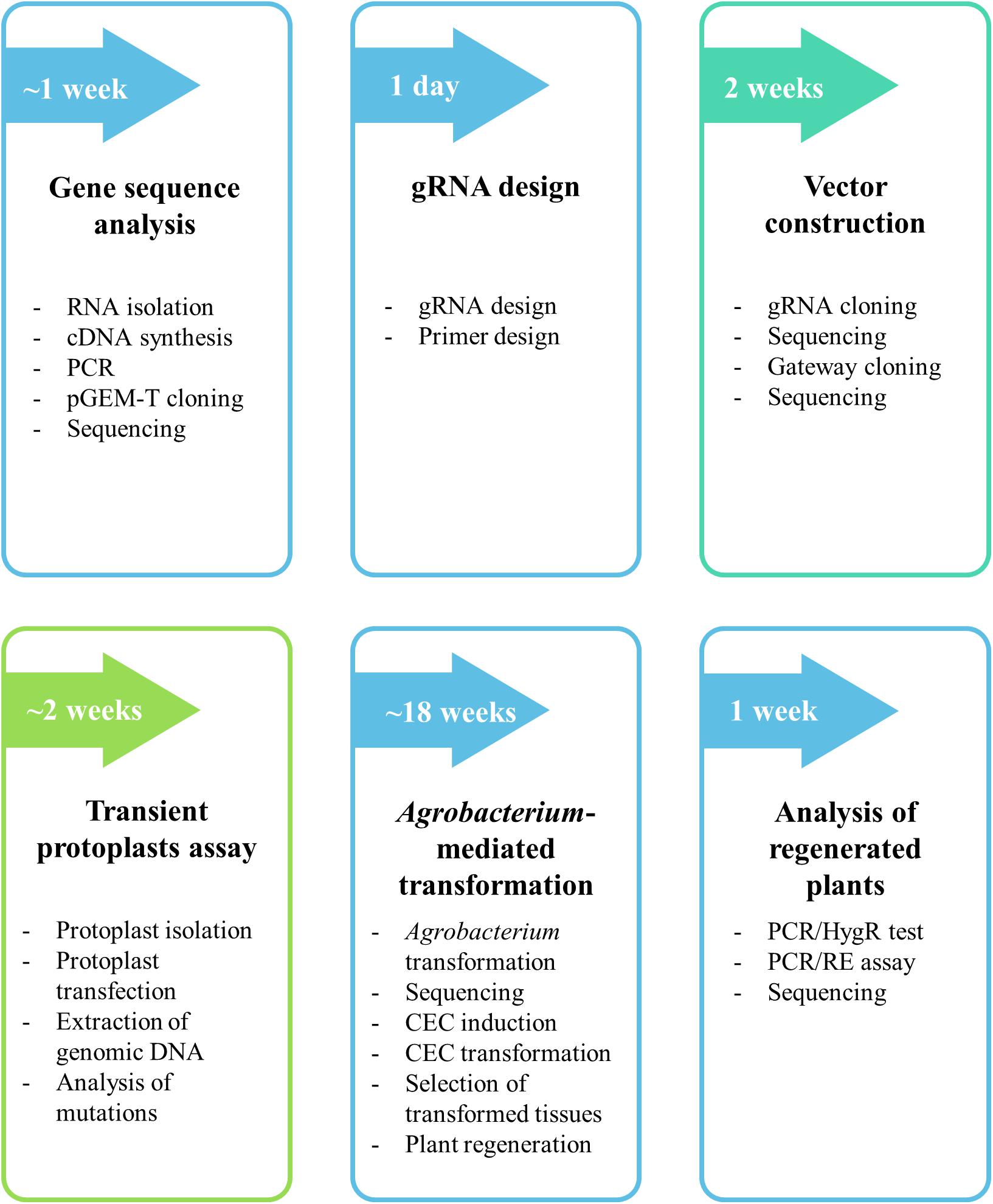
Guide RNA (gRNA) is a piece of RNAs that function as guides for RNA or DNAtargeting enzymes, which they form complexes with Very often these enzymes will delete, insert or otherwise alter the targeted RNA or DNA They occur naturally, serving important functions, but can also be designed to be used for targeted editing, such as with CRISPRCas9 The mismatch intolerant seed region of Such mutations may occur within the editing plasmid, or on the chromosome at the PAM site or the first 10–12 nt of the gRNA protospacer (known as the seed region) within which any mutations cause a severely deleterious effect on cleavage efficiency (Jiang, Bikard, Cox, Zhang, & Marraffini, 13; The group then looked beyond the 'seed' region and used structural biology and mutational analysis to examine the effects of surrounding nucleotide context on knockdown efficiency, as well as the impact of gRNA folding and secondary structures

High Efficiency Targeting Of Non Coding Sequences Using Crispr Cas9 System In Tilapia G3 Genes Genomes Genetics
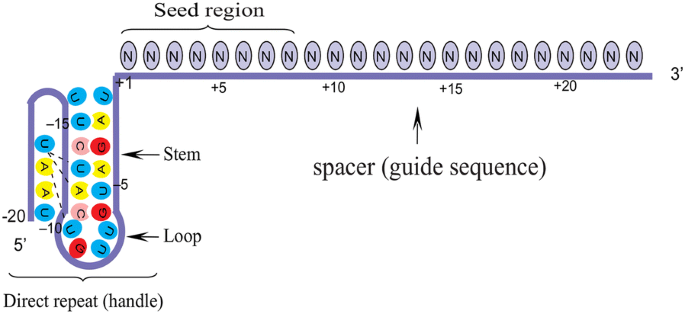
Grna seed region
Grna seed region-This mutation results in a truncated protein as seen in patients with Infantile Onset Pompe Disease (IOPD) Silent protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) site mutations (Gaa A>, Gaa A>) and a gRNA seed region mutation (Gaa T>) were also introduced to prevent gRNA editing of the donor templateThe seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementary




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
Check the search result to identify gRNA spacer sequences that could be used to target selected gene or intergeneric region; Wong et al further analyzed the dataset of Doench et al and reported that nucleotides at position 18– are the seed region of the gRNA This region and the nucleotides located at 51–53 should be unbound and accessible to form efficient gRNAs If the seed region would bind to position 51–53 of the gRNA, it would be nonfunctionalThis option allows users to calculate scores based on a particular region of the input sequences, such as the seed region of the gRNA Note that if the input sequence is longer than bp without PAM or 23 bp with PAM, only the first nucleotides are analyzed Results Page
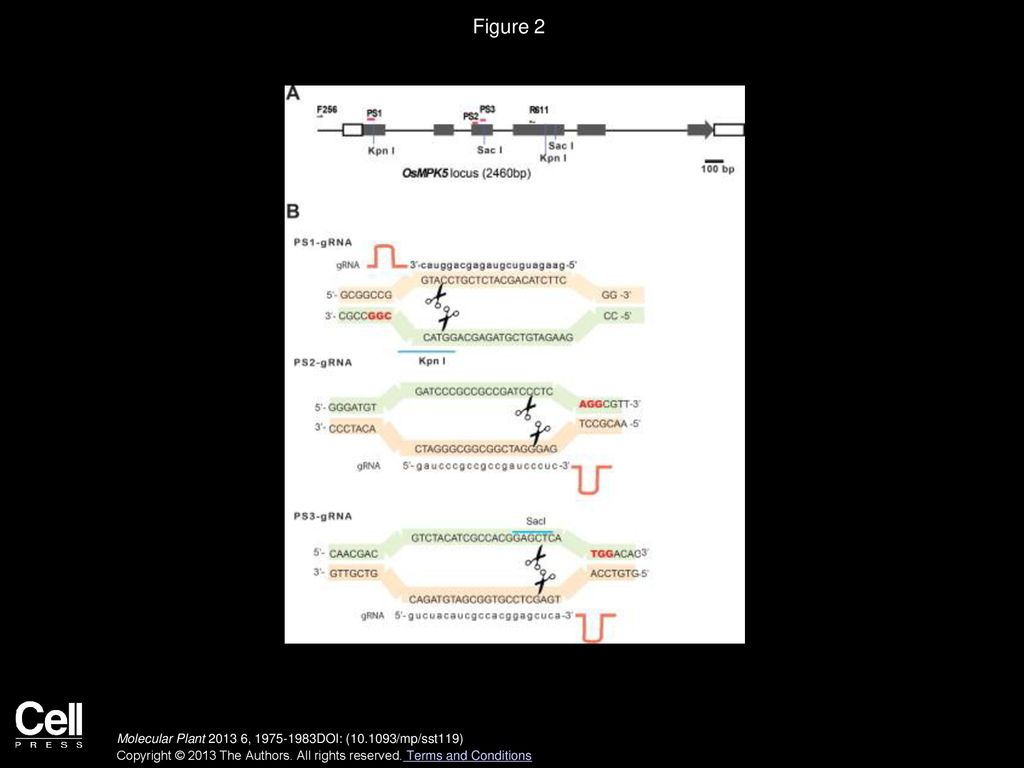
Three guide RNA (gRNA) sequences were designed based on the corresponding target sites in the OsMPK5locus (PS1, PS2, and PS3;The presence of a single mismatch within the seed region of the guide sequence greatly reduced but did not abolish gRNA activity, whereas the presence of an additional mismatch, or the absence of a PAM, all but abolished gRNA activity Large insertions (≥ bp) of DNA vectorderived sequence were detected at frequencies up to 85% of totalIt is important for gRNA to interact initially with preedited mRNA and then its 5' region base pair with complementary mRNA The 3' end of gRNA contains oligo 'U' tail (525 nucleotides in length) which is a non encoded region but interacts and forms a stable complex with A and G rich regions of mRNA
Herein, unlike previous engineering of gRNA that generally focused on the RNA part only but neglected RNA–protein interactions, we aimed at the interactive sites between 2′OH of ribose in the seed region of gRNA and the Cas9 protein and identified that chemical modifications at specific sites could be utilized to regulate the Cas9 activityThe sequence beyond the seed region also confers target specificity However, two mismatches (eg, in the case of egfp OT1) could be tolerated These results are consistent with a recent study by Fu et al No 1 seed Central bested rival Red River, the No 2 seed, 32 in the title match In state qualifiers, No 3 seed Fargo South defeated No 5 seed Fargo Davies 32, and No 4 seed




The Neisseria Meningitidis Crispr Cas9 System Enables Specific Genome Editing In Mammalian Cells Molecular Therapy




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Sciencedirect
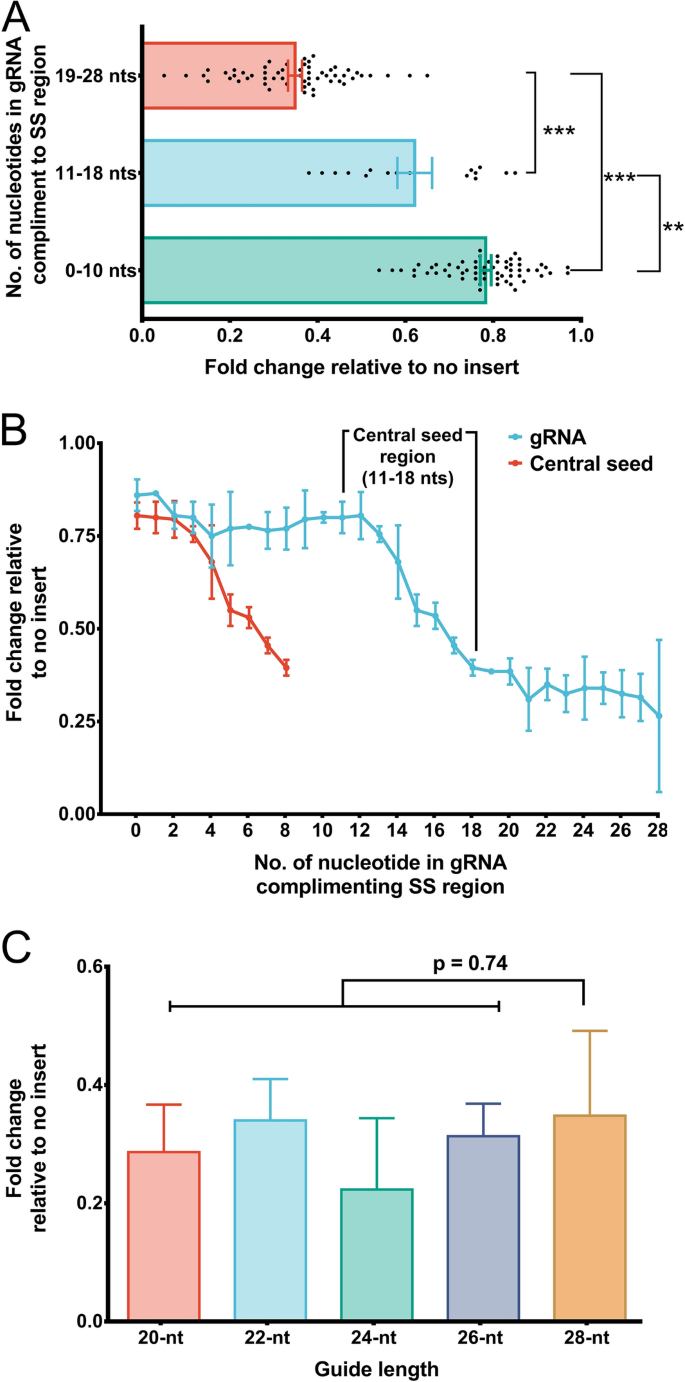
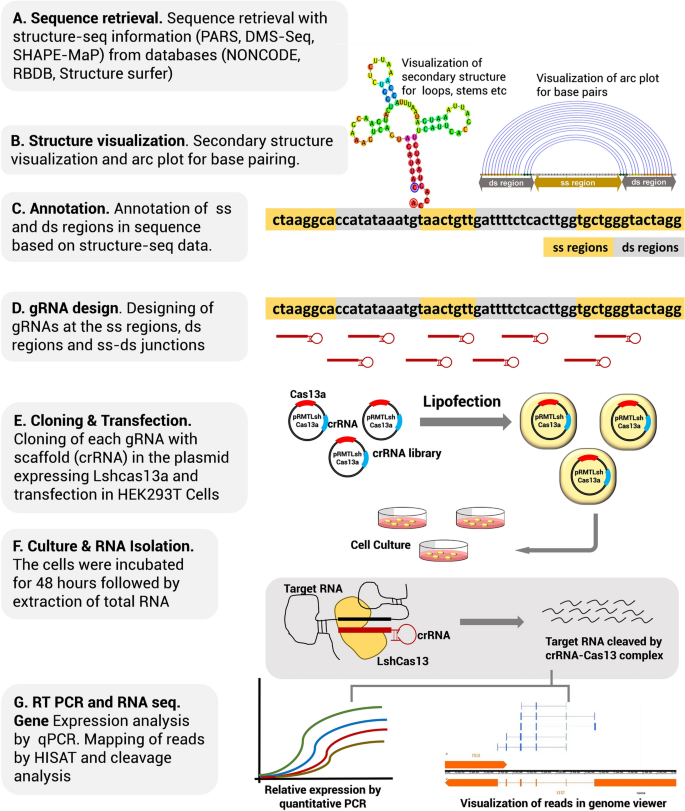
Figure 2A) The PS1–gRNA seed region (22 nt) was predicted to pair with the template strand of OsMPK5, and would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a KpnI siteIf gRNA expression is too high, reduction can be accomplished by inclusion of a UUU stretch in the seed region, which may lead to partial transcriptional termination and lower expression levels (Wu et al 14) Given the higher degree of specificity in plants, it is unlikely that gRNA expression levels are a general concernThe central segment (in Red) in the gRNA is the central seed region (Right) SS and DS stranded regions in the RNA structure are shown as arc plot, along with the targeting gRNAs gRNAs (a,




Binding Of Central Seed Region In Grna Crucial For Cas13 Mediated Download Scientific Diagram




Single Base Resolution Increasing The Specificity Of The Crispr Cas System In Gene Editing Sciencedirect
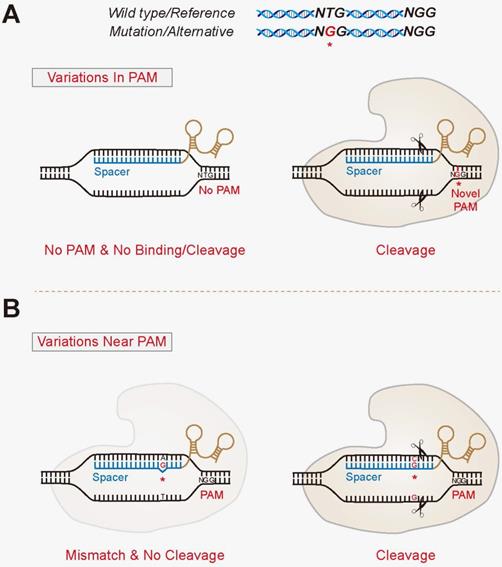
CRISPRCas9 is a simple twocomponent system that allows researchers to precisely edit any sequence in the genome of an organism This is achieved by guide RNA, which recognizes the target sequence, and the CRISPRassociated endonuclease (Cas) that cuts the targeted sequence Researchers across the globe who are adopting this technology are bound to come across an important term PAM sequenceMaximum number of mismatches in seed region tolerated by off targets Seed region stands for 6 nucleotides in the 5' PAMproximal region (Kim et al, 17) Relative to the target candidate sequence, sequences with more than this number of mismatches in the seed region will be excluded from consideration of offtarget effects Tilapia miRNA125 was selected as the target to examine whether mutation could be induced in the seed region using CRISPR/Cas9 gRNA containing restriction enzyme Mse I was designed in the seed sequence of miRNA125 Coinjection of gRNA and Cas9 mRNA led to indels formation in the seed region



A Cas9 Is Directed To A Specific Genomic Target By The First Nt Of Download Scientific Diagram



Crispr Cpf1 Proteins Structure Function And Implications For Genome Editing Springerlink
It was suggested that the gRNA sequence of CRISPRCpf1 should be divided into seed (6 nt in the 5' PAMproximal end) and nonseed (14 nt in the 3' PAMdistal end) regions (Kim et al, 17b, 18) The tolerant ability of mismatches in the seed region is lower than that in the nonseed region seed region alone on the gRNA (ie, 1112 bases before the PAM) is not sufficient to guide the Cas9 cleavage; It is, in fact the, the "central seed" binding region in the gRNA with 8 central bases (11–18 nts) which upon complementing SS region in the




Crispr Cas Systems In Genome Editing Methodologies And Tools For Sgrna Design Off Target Evaluation And Strategies To Mitigate Off Target Effects Manghwar Advanced Science Wiley Online Library
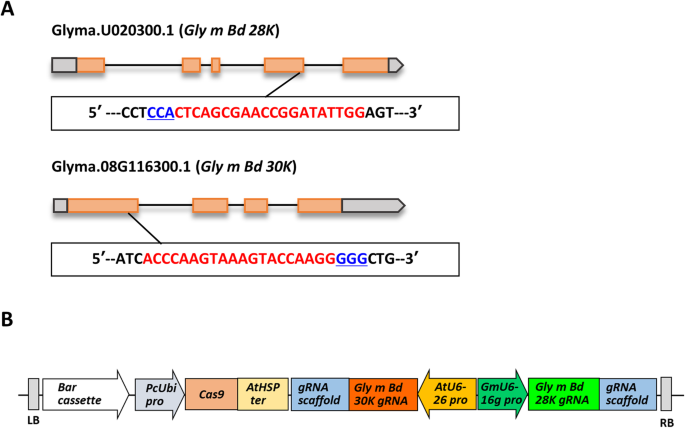



Simultaneous Induction Of Mutant Alleles Of Two Allergenic Genes In Soybean By Using Site Directed Mutagenesis Bmc Plant Biology Full Text
The guide RNA is a specific RNA sequence that recognizes the target DNA region of interest and directs the Cas nuclease there for editing The gRNA is made up of two parts crispr RNA (crRNA), a 17 nucleotide sequence complementary to the target DNA, and a tracr RNA, which serves as a binding scaffold for the Cas nucleaseEukaryotic Pathogen CRISPR guide RNA/DNA Design Tool with (1) custom genome upload, (2) offtarget analysis, (3) ontargets searching (for targeting gene families), (4) efficiency/activity prediction, (5) assisted oligo repair template design , (6) guide RNA transcription problem identification, (7) flanking microhomology searching (forIn addition, we examined UUU in the gRNA seed region, which are the 6 nucleotides in the 5' PAMproximal region 41, and found that more inefficient gRNAs contains UUU in the seed region than efficient ones with an enrichment ratio of 029 (P = 907E02), which is consistent with previous CRISPRCas9 research 48
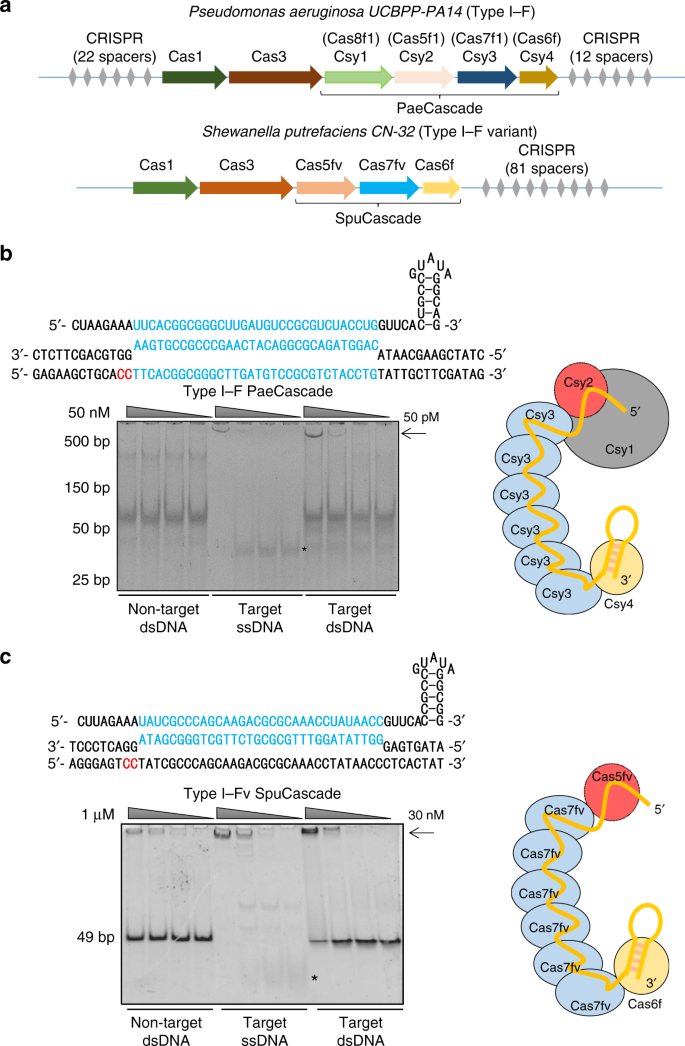



Repurposing Type I F Crispr Cas System As A Transcriptional Activation Tool In Human Cells Nature Communications




Addgene Crispr Guide
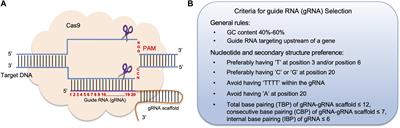
GRNA targeting region of interest gRNA targeting gene promoter elements gRNA targeting gene promoter elements Table 2 Plasmid Vector Expression System Components Applica with matches in the "seed" region of the mer recognition site, which lies adjacent to the PAM MoreSeveral features were mentioned to enhance gRNA e ectiveness 17,18 the last three base pairs of the gRNA (seed region) should be unpaired and freely accessible 18; The NP390 gRNA 14 specifically has its critical seed region (nt2nt4) directly complementing a pseudoknot These three preRISC gRNA nts are essential for initially recognizing the target mRNA 15
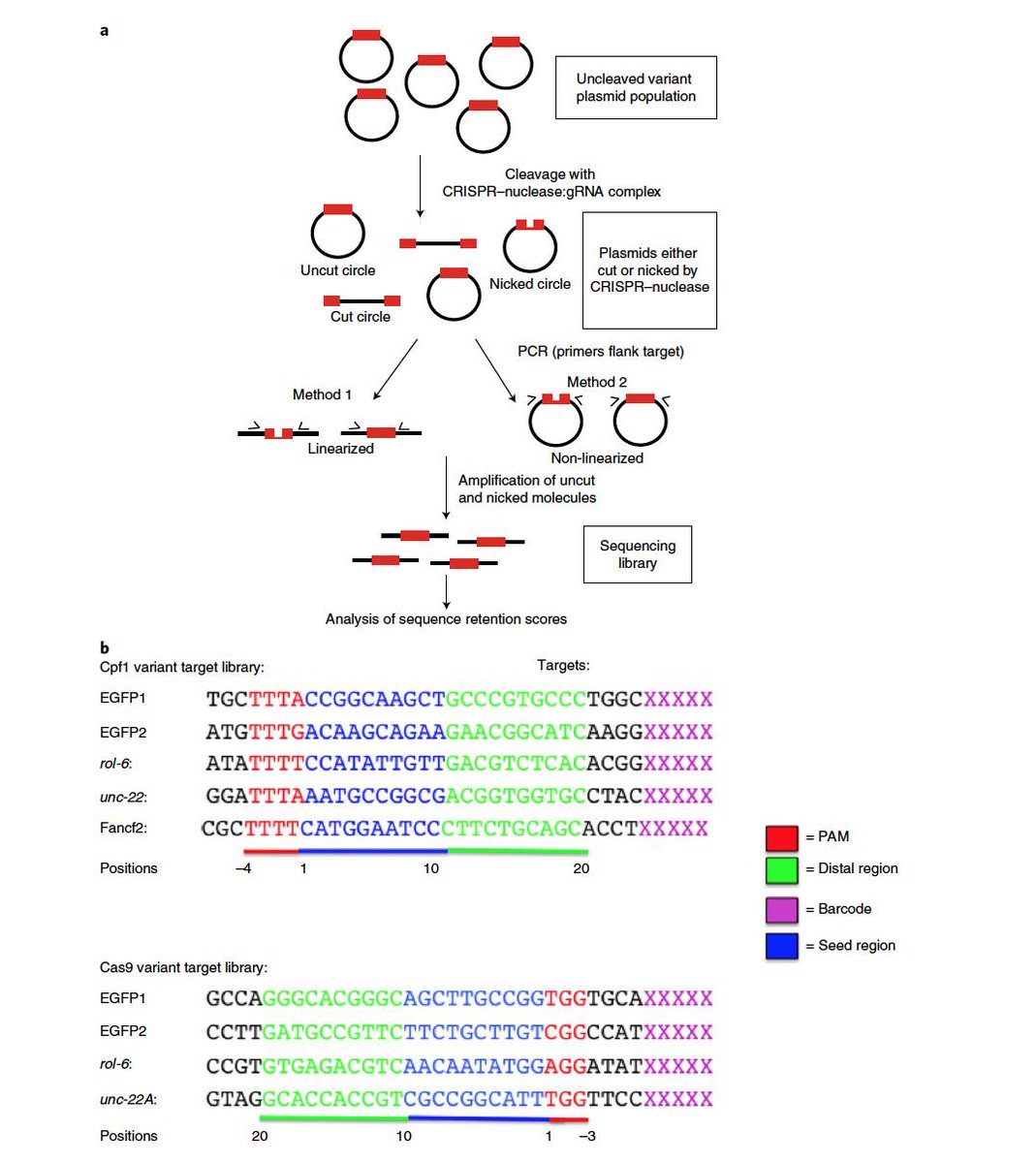



Dr Gaetan Burgio Md Phd Interesting This Paper Published Today In Naturemicrobiol Shows That Crispr Cas9 Or Cas12a Cpf1 Can Display An Inherent Potent Nicking Activity In Yeast This Nicking
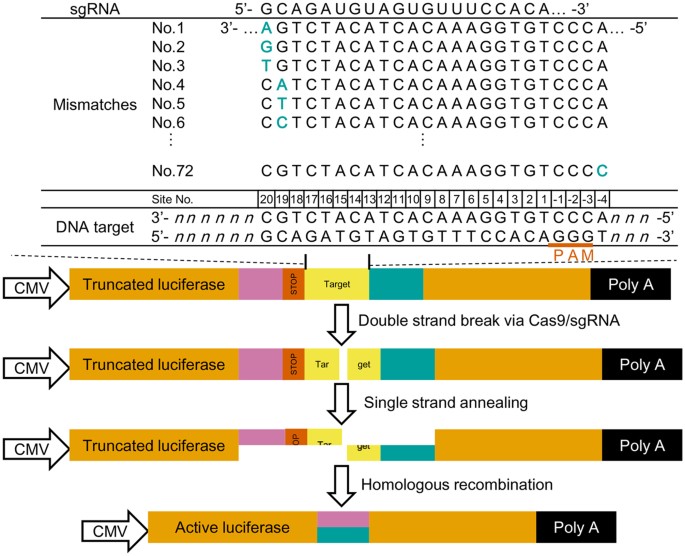



Profiling Single Guide Rna Specificity Reveals A Mismatch Sensitive Core Sequence Scientific Reports
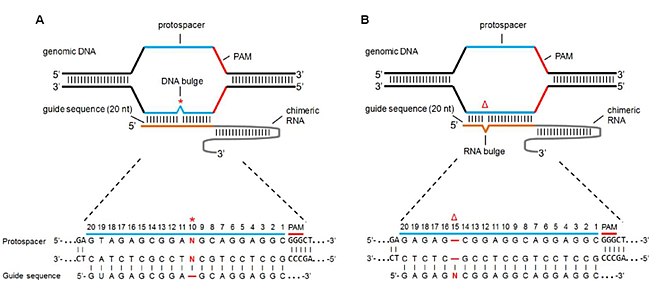
Accompanies basepairing in the PAMdistal region, activating the endonuclease, and cutting both strands of DNA upstream of position 3 in the protospacer (7) One consequence of the zipping model is that the gRNAprotospacer duplex can be divided into two functional domains Basepairing within the seed, or PAMproximal region (positions 110),Currently, CRISPRPLANT will show all Class00 and Class10 gRNA spacer sequences We will add other gRNA spacer information in the near future Following information will be listed for each spacer sequencePAM (seed region) are especially important for target site recognition In many cases, offtarget mutations happen at sites where the gRNA seed region has no mismatches but the nonseed region does 3, 15 To knock out a specific region in the genome, such offtarget effects should be avoided Reducing such risk is espe




An Efficient Targeted Mutagenesis System Using Crispr Cas In Monocotyledons Liang 16 Current Protocols In Plant Biology Wiley Online Library
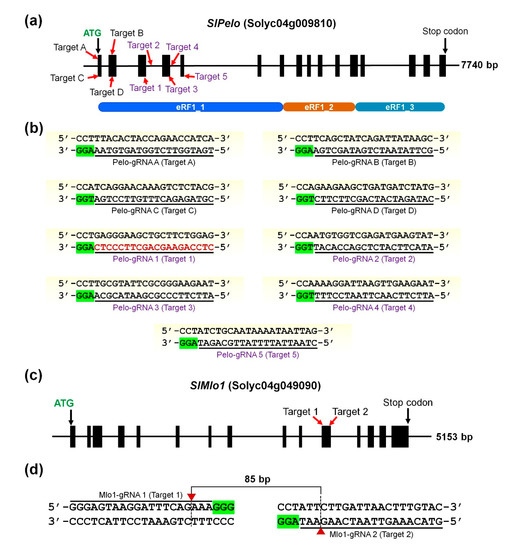



Ijms Free Full Text Crispr Cas9 Mediated Generation Of Pathogen Resistant Tomato Against Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus And Powdery Mildew Html
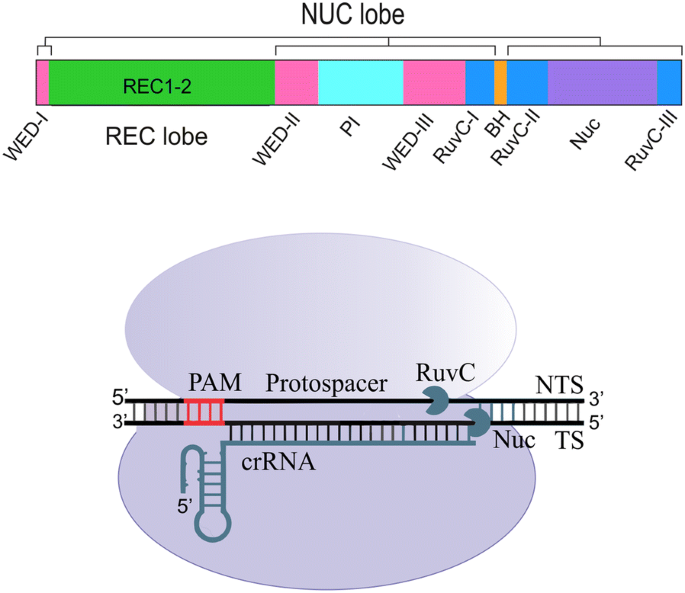
Matches within the gRNA and reported varying degrees of specificity within the bases that constitute the spacer sequence Consistent with previous studies, they reported that mismatches within the PAMdistal region are more tolerated and defined a range of 8 to 14 bases in the PAMproximal region as the seed sequence that providesImportantly, the spacer region of the gRNA remains free to interact with target DNA Cas9 will only cleave a given locus if the gRNA spacer sequence shares sufficient homology with the target DNA Once the Cas9gRNA complex binds a putative DNA target, the seed sequence (810 bases at the 3′ end of the gRNA targeting sequence) will begin to anneal to the target DNA The seed segment of gRNA and PAM are two elements that determine Cpf1 specificity It seems that Cpf1 has a lower threshold for nonseed mismatches visavis Cas9 Seed region flanks at the initial part of the spacer and plays a notable role in the target specificity of CRISPR–Cpf1 system (Fig




A Meta Analysis Of Grna Library Screens Enables An Improved Understanding Of The Impact Of Grna Folding And Structural Stability On Crispr Cas9 Activity Biorxiv
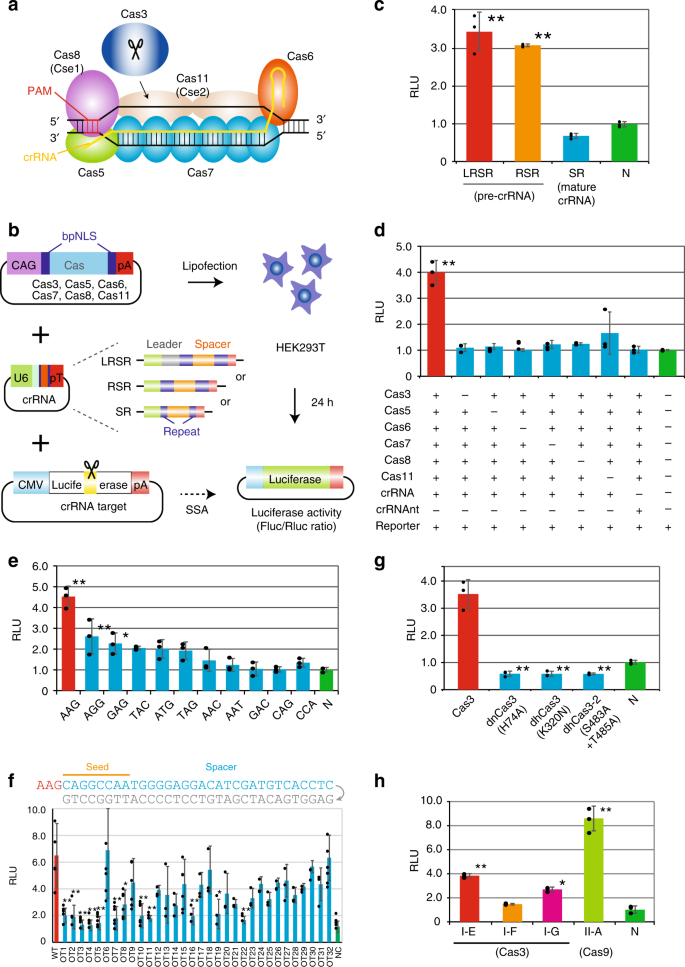



Crispr Cas3 Induces Broad And Unidirectional Genome Editing In Human Cells Nature Communications
Jinek et al, 12)(B) (Left) Schematic illustrating gRNAs targeting the SS and DS regions in the RNA structure The central segment (in Red) in the gRNA is the central seed regionCasbased technology is gRNA design The DNA, unwound by Cas9, is probed by the gRNA sequence adjacent to the PAM13,14 The first few nucleotides are referred to as the ''seed'' sequence, where Cas9 is most sensitive to mismatches If there is full seed region complementarity, Cas9 is more likely to remain bound to the




High Efficiency Targeting Of Non Coding Sequences Using Crispr Cas9 System In Tilapia G3 Genes Genomes Genetics
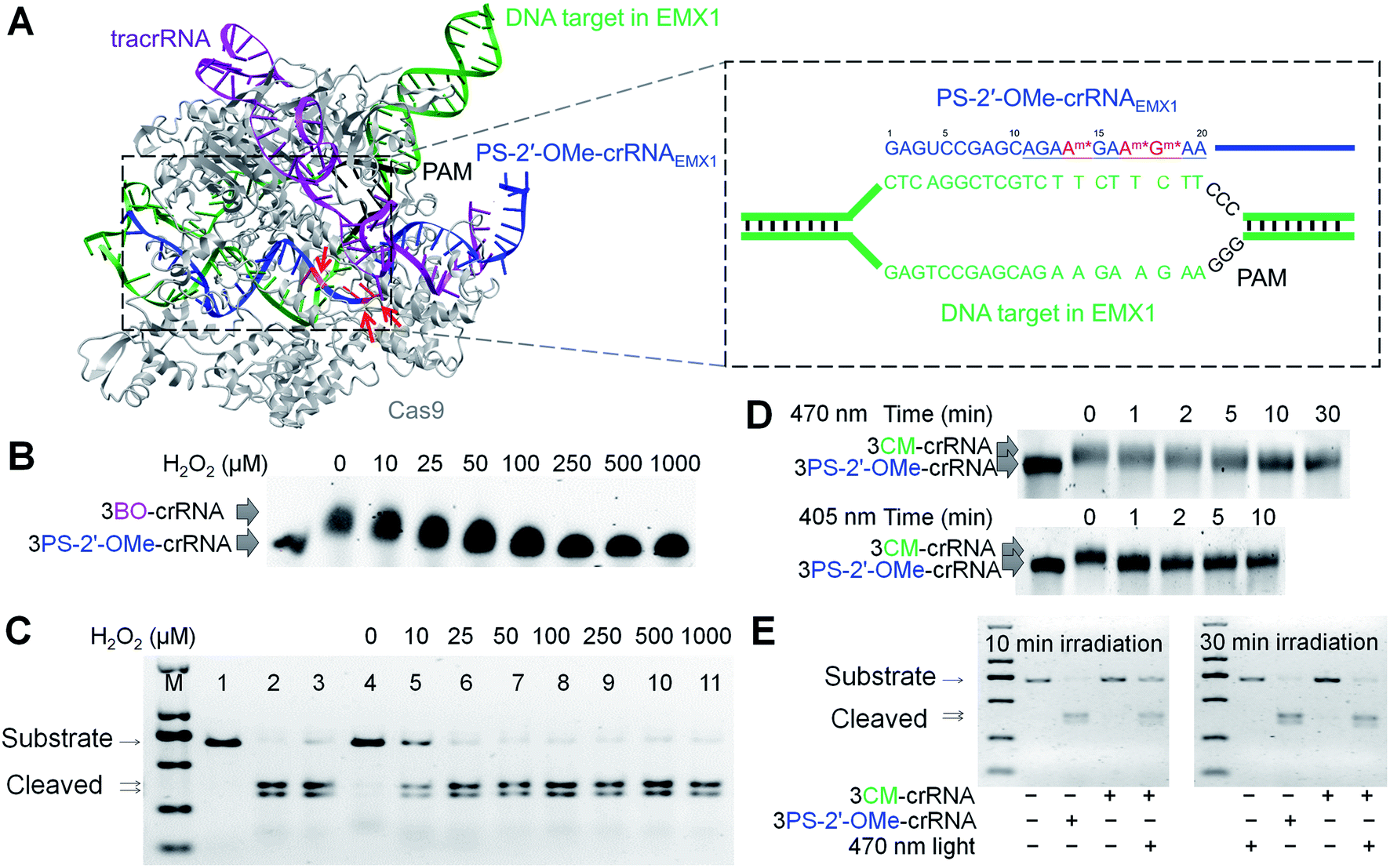



Chemical Synthesis Of Stimuli Responsive Guide Rna For Conditional Control Of Crispr Cas9 Gene Editing Chemical Science Rsc Publishing
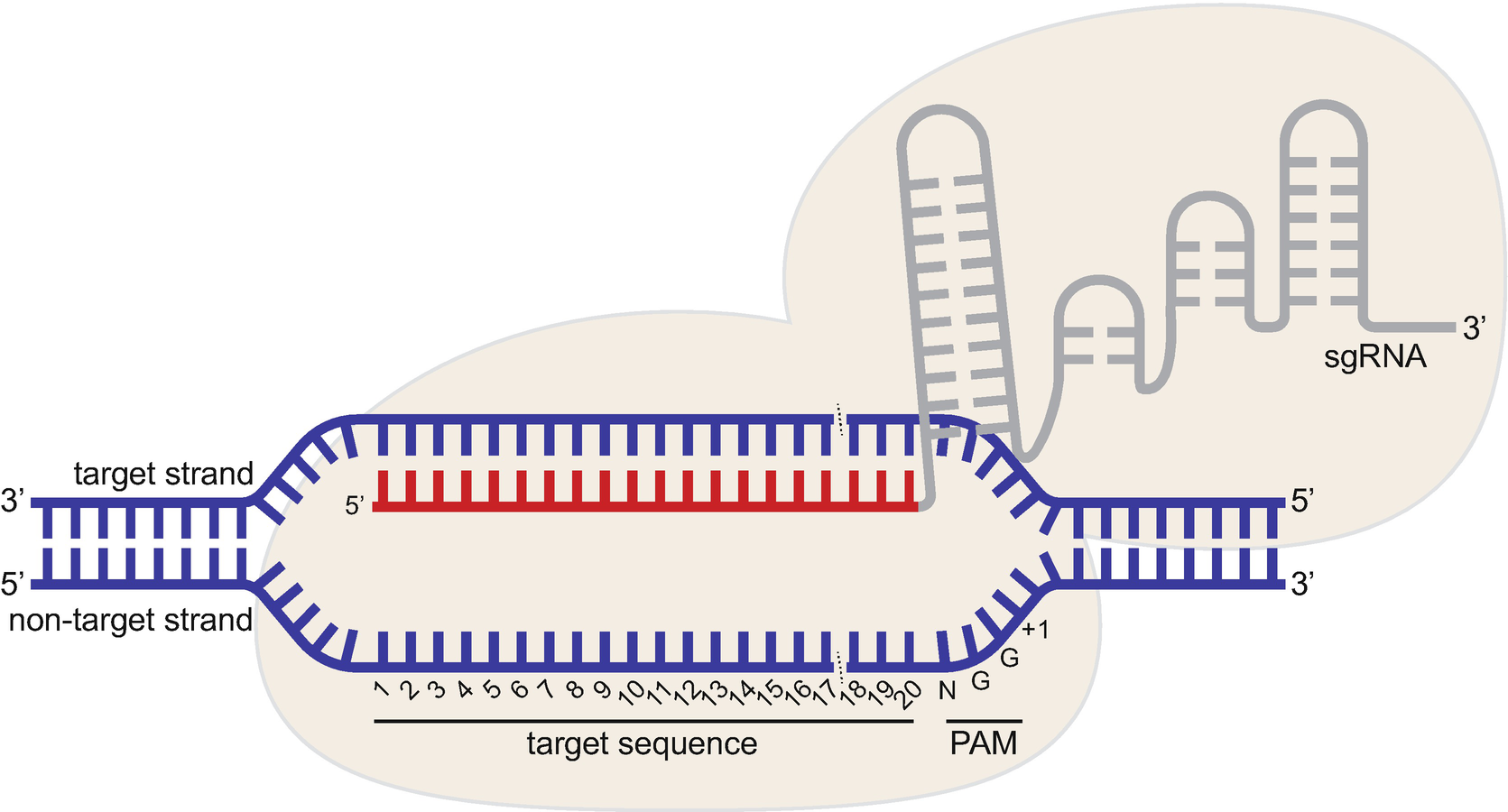
Red indicates the seed region that is less tolerance to mismatches for Cas9 binding b The flowchart of the bioinformatics analysis procedure to evaluate gRNA specificities The guide sequences of gRNA that target rice mitochondrial and chloroplast 16S rRNA gene (mtgRNA and cpgRNA) were extracted according to the requirements for Cas9/gRNA The 3′ end of the guide sequence, also known as the "seed region", plays a critical role in recognition of target sequence Thus, based on structural analysis, accessibility of the last three bases in the seed region was a prominent feature to differentiate functional sgRNAs from nonfunctional ones (Fig 1b ) This system consists of the Cas9 endonuclease in complex with a small guide RNA (gRNA) that is engineered to target a specific site in the genome The target site is defined by a nucleotide guide sequence at the 5′ end of the gRNA, making programming of




Programmable Rna Recognition Using A Crispr Associated Argonaute Pnas




Crispr Cas9 Mediated Gene Modification And Gene Knock Out In The Human Infective Parasite Trichomonas Vaginalis Abstract Europe Pmc
Cas9 nucleases can be programmed with single guide RNAs (sgRNAs) to mediate gene editing High CRISPR/Cas9mediated gene knockout efficiencies are essential for genetic screens and critically depend on the properties of the sgRNAs used The specificity of an sgRNA is defined by its targeting sequence Here, we discovered that two short sequence The PS1–gRNA seed region (22 nt) was predicted to pair with the template strand of OsMPK5, and would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a KpnI site The PS2– and PS3–gRNA seeds region ( and 22 nt, respectively) were predicted to pair with the coding strand of OsMPK5, and PS3–gRNA would guide Cas9 to make DSB at a SacI site Subsequently, three gRNA–Cas9Wong et al further analyzed the dataset of Doench et al and reported that nucleotides at position 18– are the seed region of the gRNA This region and the nucleotides located at 51–53 should be unbound and accessible to form efficient gRNAs If the seed region would bind to position 51–53 of the gRNA, it would be nonfunctional



Full Article Defining The Seed Sequence Of The Cas12b Crispr Cas Effector Complex



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Design Rules For Predicting Activity Springerlink
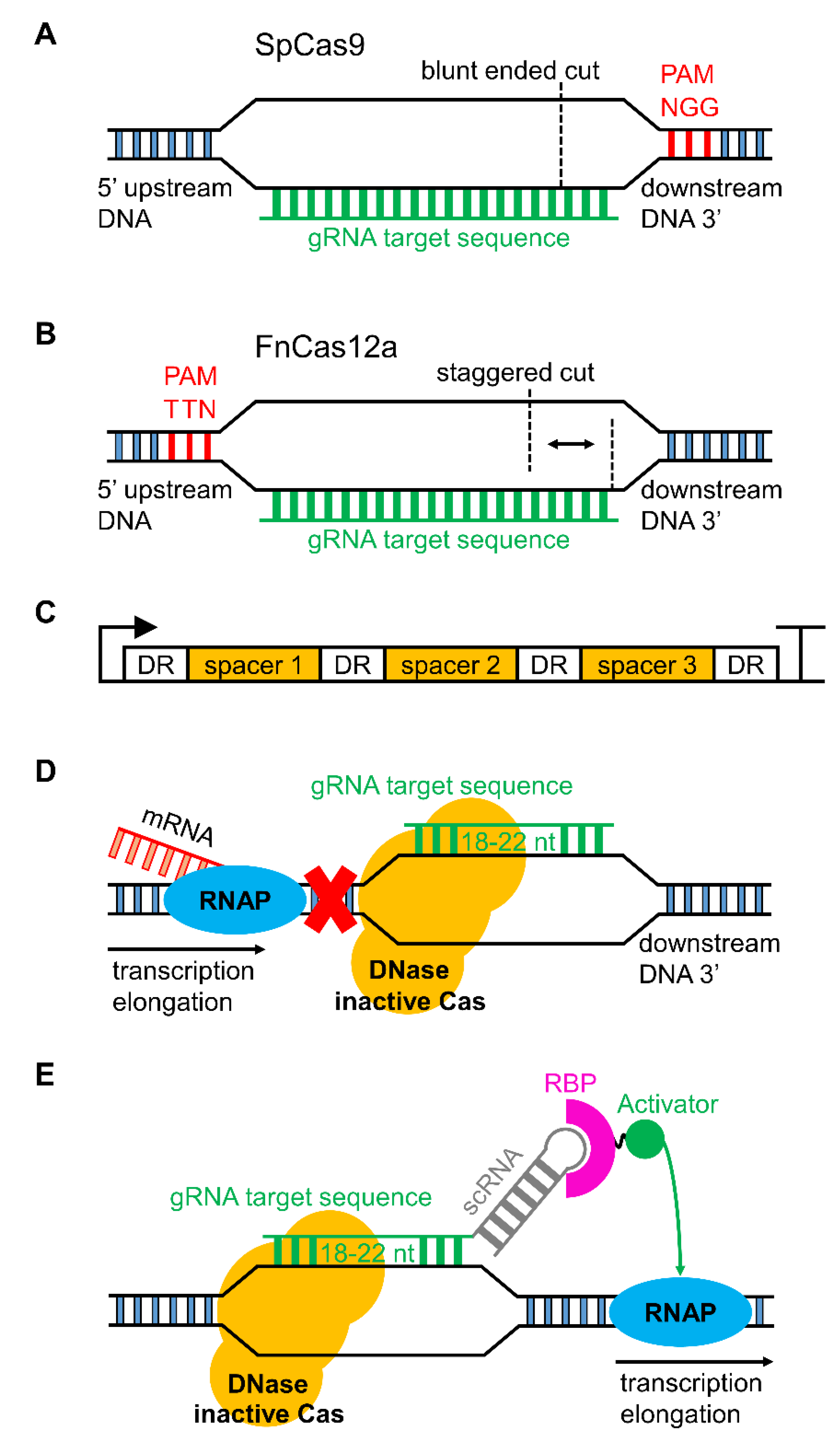
Truncating gRNA Length 16 Fu Y et al Improving CRISPRCas nuclease specificity using truncated guide RNAs Nat Biotech (14) gRNA sequences can be 17 nt in length to achieve similar levels of ontarget gene editing Up to 10,000 fold improvement in target specificity when truncated (17 or 18 base pair) gRNA is usedThe complex then scans the DNA for a complementary sequence to the nucleotides on its 5′ end, termed the guide region (spacer region), with an adjacent upstream protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequence (5′NGG3′ in S pyogenes) ( Jiang and Doudna, 17 ) Investigation into SpCas9 specificity has revealed that both the 612 nt seed region of the gRNA recognition sequence and the adjacent PAM are important for nuclease activity 1314,17 Off target mutations can be minimized by ensuring that the seed region and adjacent PAM are unique in the genome being modified 14,16



2




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Molecular Plant
Nucleotides 51–53 of the tracrRNA should be not paired to the seed region and be freely accessible, and there should be favorable nucleotides at several positions 17 The seed sequence in the gRNA contributes greatly to the specificity of Ago RNP interactions with target substrates The canonical seed region of all eAgos and some pAgos is composed of the second to eighth nts of the gRNA and has an Aform helical conformation in the Ago RNP complex (18 ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ ⇓ –23)CasFinder Guide RNA design for the CRISPR/Cas9 system Genome Mp JGI 31 MpTak1 v51 Search conditions Length of gRNA 18 nt, Seed Region 9 nt, Primary/secondary PAM NGG/NAG Length of gRNA nt, Seed Region 8 nt, Primary/secondary PAM NGG/NAG Enter your sequence (s) in FASTA format below (Please make your sequence as short as possible!




Design And Synthesis Of Grna A Design Of Grna Dna Template Mix The Download Scientific Diagram



Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia
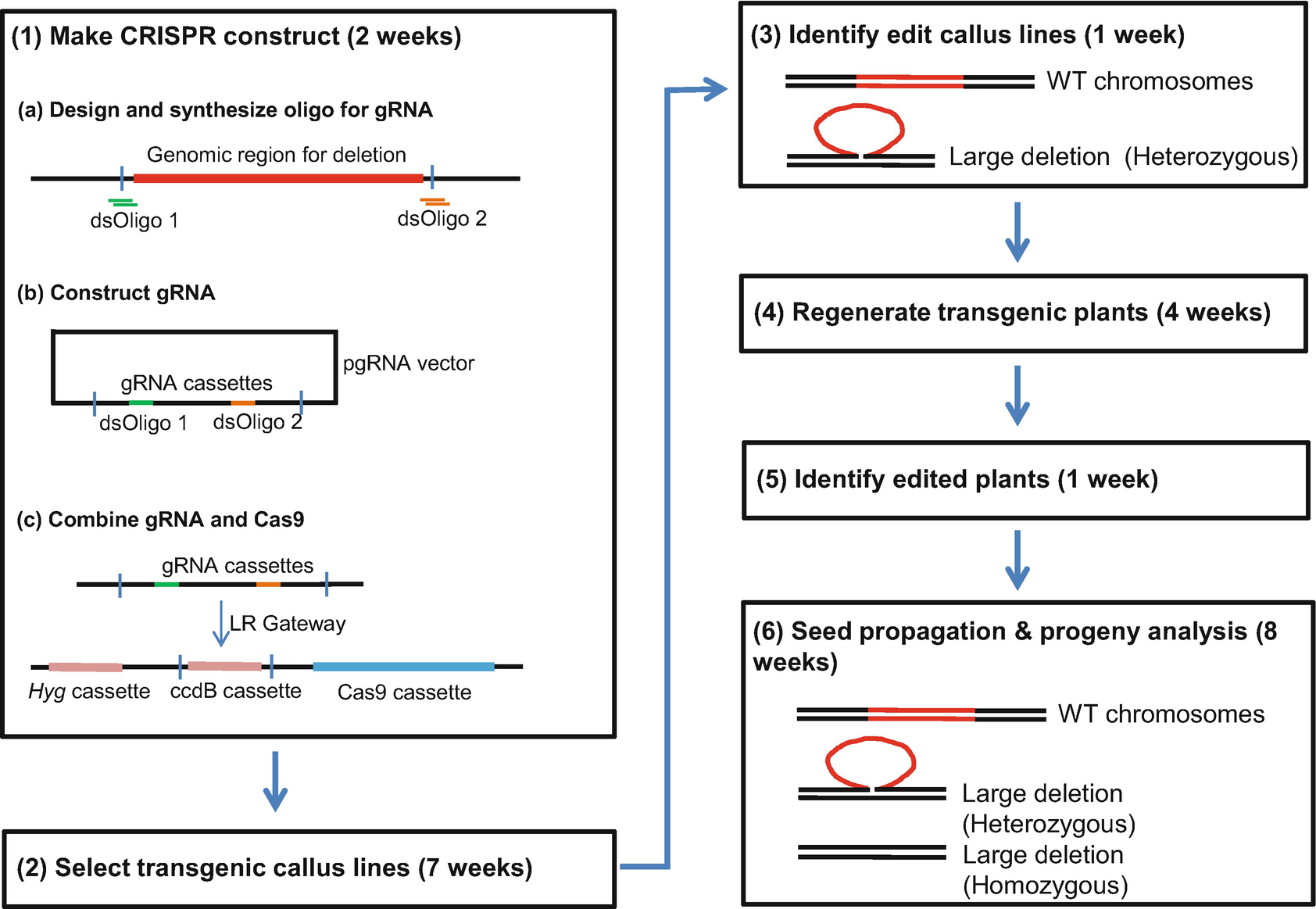



Creating Large Chromosomal Deletions In Rice Using Crispr Cas9 Springerlink




Crispr Vae A Method For Explaining Crispr Cas12a Predictions And An Efficiency Aware Grna Sequence Generator Biorxiv



Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Ppt Download



Casot A Genome Wide Potential Cas9 Grna Off Target Searching Tool



Tsl Synbio




Crispr Cas9 Gene Drives In Genetically Variable And Nonrandomly Mating Wild Populations




Target Dependent Nickase Activities Of Crispr Cas Nucleases Cpf1 And Cas9 Semantic Scholar




Modification Of Cas9 Grna And Pam Key To Further Regulate Genome Editing And Its Applications Sciencedirect
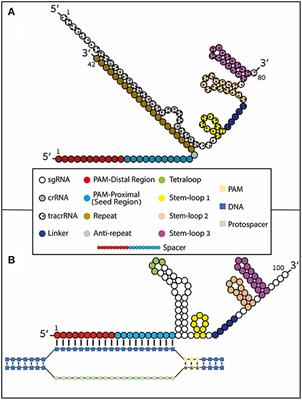



Frontiers Using Synthetically Engineered Guide Rnas To Enhance Crispr Genome Editing Systems In Mammalian Cells Genome Editing



Casot A Genome Wide Potential Cas9 Grna Off Target Searching Tool




Target Dependent Nickase Activities Of The Crispr Cas Nucleases Cpf1 And Cas9 Abstract Europe Pmc




Crispr Plant




Schematics Of Cas9n Grna Target Sequence Specific Fluorescent Download Scientific Diagram



View Of A Streamlined Crispr Cas9 Approach For Fast Genome Editing In Toxoplasma Gondii And Besnoitia Besnoiti Journal Of Biological Methods




Engineered Rna Interacting Crispr Guide Rnas For Genetic Sensing And Diagnostics The Crispr Journal



1



2
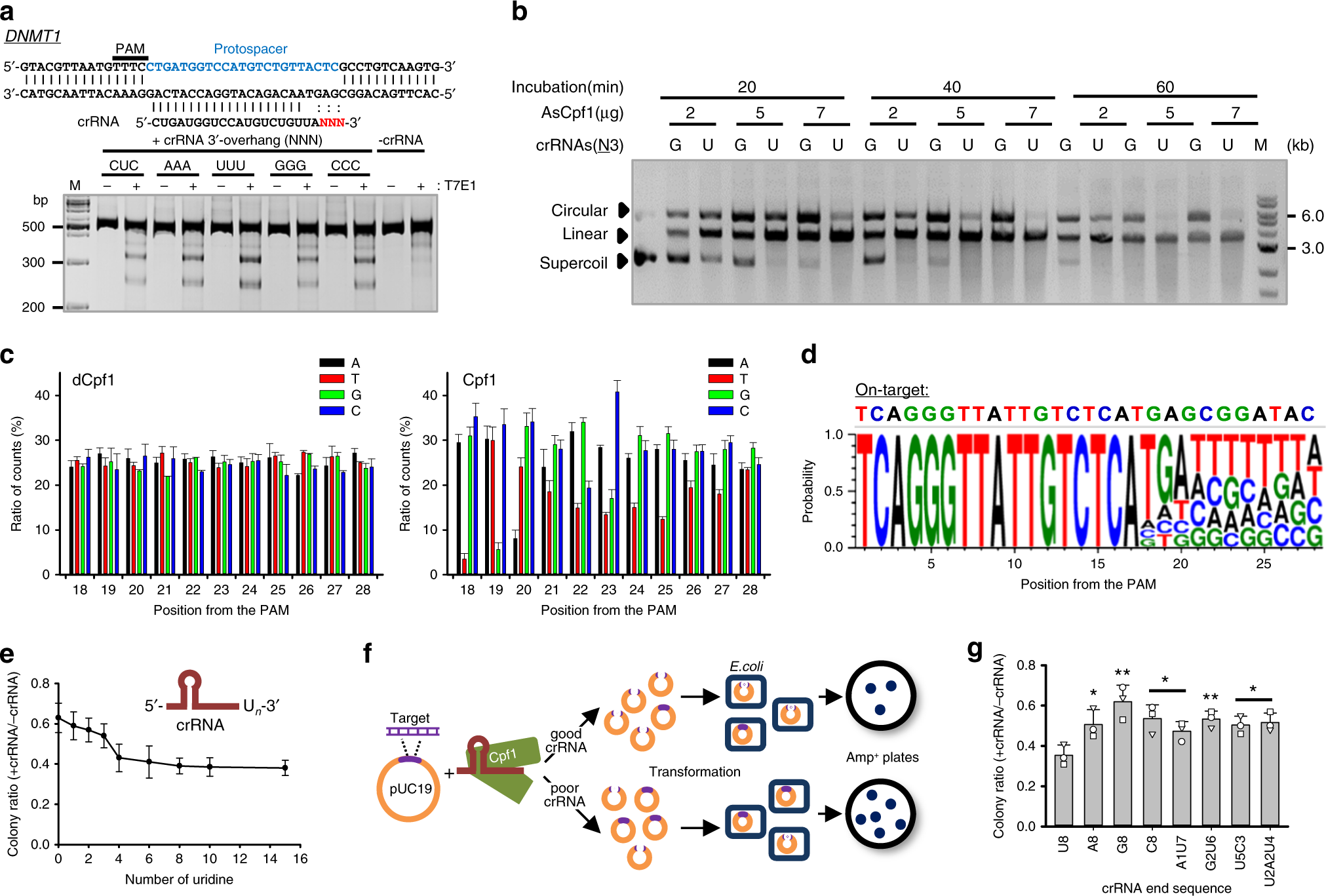



Highly Efficient Genome Editing By Crispr Cpf1 Using Crispr Rna With A Uridinylate Rich 3 Overhang Nature Communications



Gene Editing



2



1




Crispr Enabled Tools For Engineering Microbial Genomes And Phenotypes Tarasava 18 Biotechnology Journal Wiley Online Library
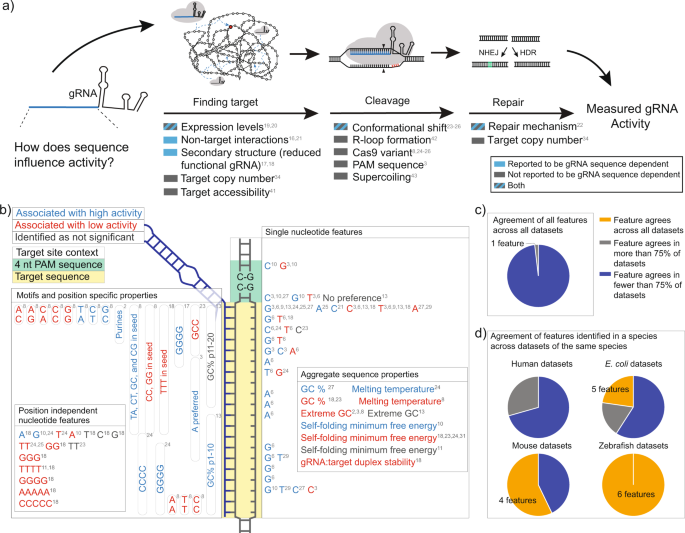



Genome Dependent Cas9 Grna Search Time Underlies Sequence Dependent Grna Activity Nature Communications




Genomic Sequences Bound By Cas9 Grna Comprehensive List Of Sequences Download Scientific Diagram




Addgene Crispr Guide
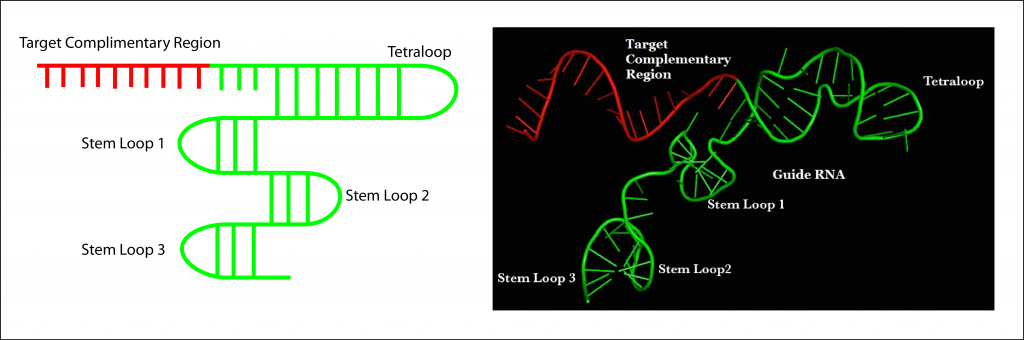



Cas9 Mechanism Crispr Cas9




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc



2




Off Target Effects In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Engineering Sciencedirect




Woa1 Gene Targeting And Genetic Modification Of Plants Via Rna Guided Genome Editing Google Patents



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports




Rna Guided Genome Editing In Plants Using A Crispr Cas System Sciencedirect




Type Ii Crispr Formulations Grnas Contain 4 Loop Structures Download Scientific Diagram




Crispr Plant




Addgene Crispr Guide



Microorganisms Free Full Text Emerging Species And Genome Editing Tools Future Prospects In Cyanobacterial Synthetic Biology Html



Plant Crispr Database




Off Target Genome Editing Wikipedia



Crispr Grna Guide Rna Design Tool For Eukaryotic Pathogens




Crispr Cas9 Mediated Exonic Disruption For Hiv 1 Elimination Ebiomedicine




Evaluating The Cleavage Efficacy Of Crispr Cas9 Sgrnas Targeting Ineffective Regions Of Arabidopsis Thaliana Genome Peerj




Efficient Multiplex Biallelic Zebrafish Genome Editing Using A Crispr Nuclease System Pnas



Crispr Cpf1 Proteins Structure Function And Implications For Genome Editing Cell Bioscience Full Text
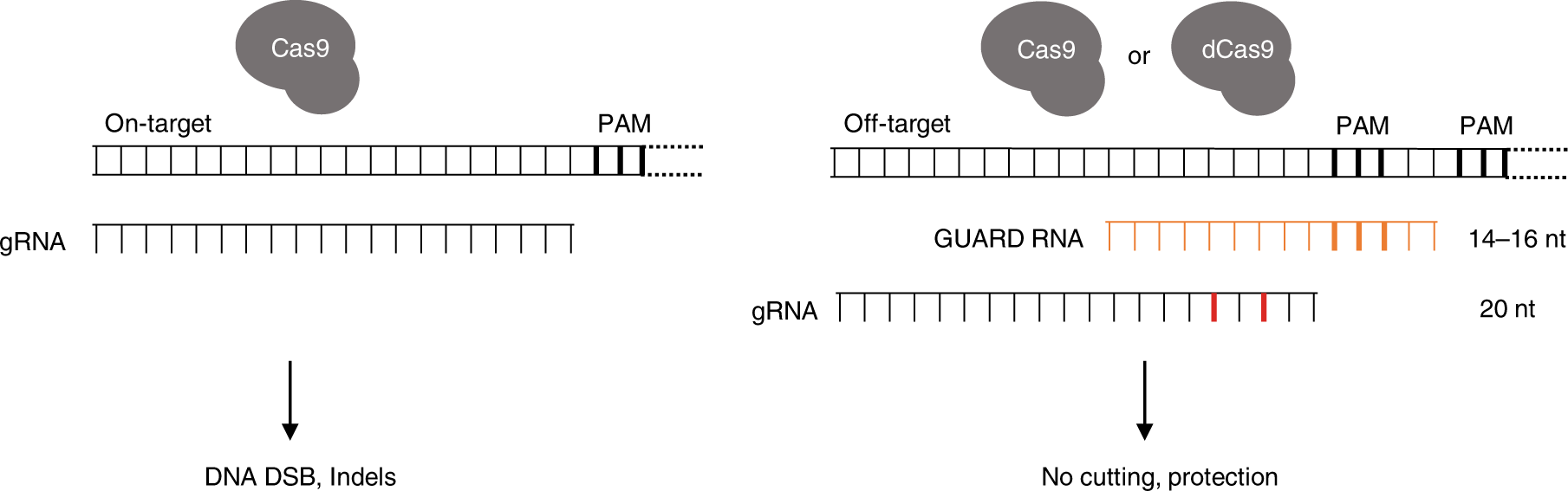



Crispr Guard Protects Off Target Sites From Cas9 Nuclease Activity Using Short Guide Rnas Nature Communications



2
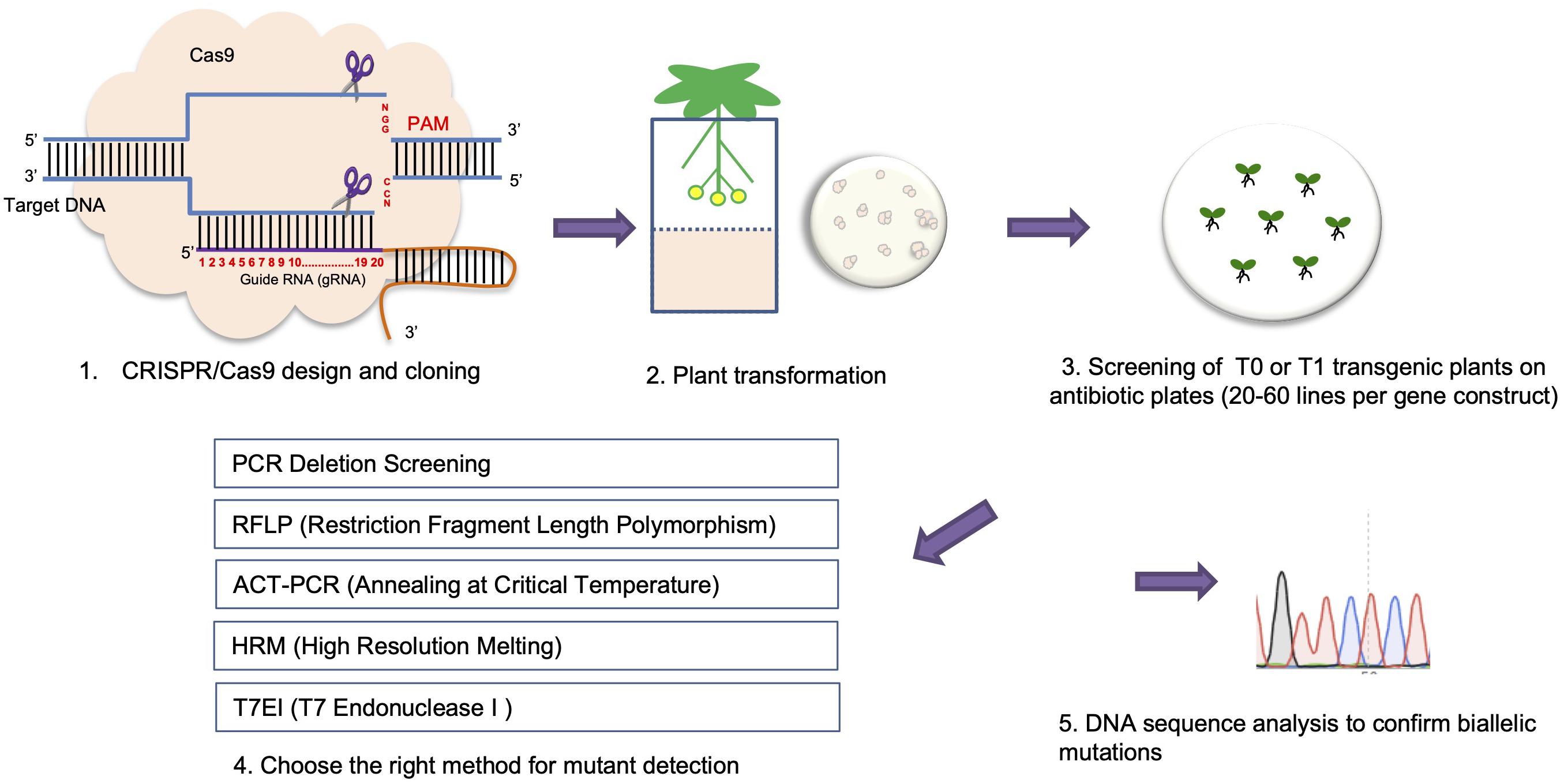



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science



2



2




Dual Sgrna Based Targeted Deletion Of Large Genomic Regions



2




Sample Input File And Possible Off Target Types In The Casot Download Scientific Diagram




Sgrna Sequence Motifs Blocking Efficient Crispr Cas9 Mediated Gene Editing Sciencedirect




Dual Sgrna Based Targeted Deletion Of Large Genomic Regions
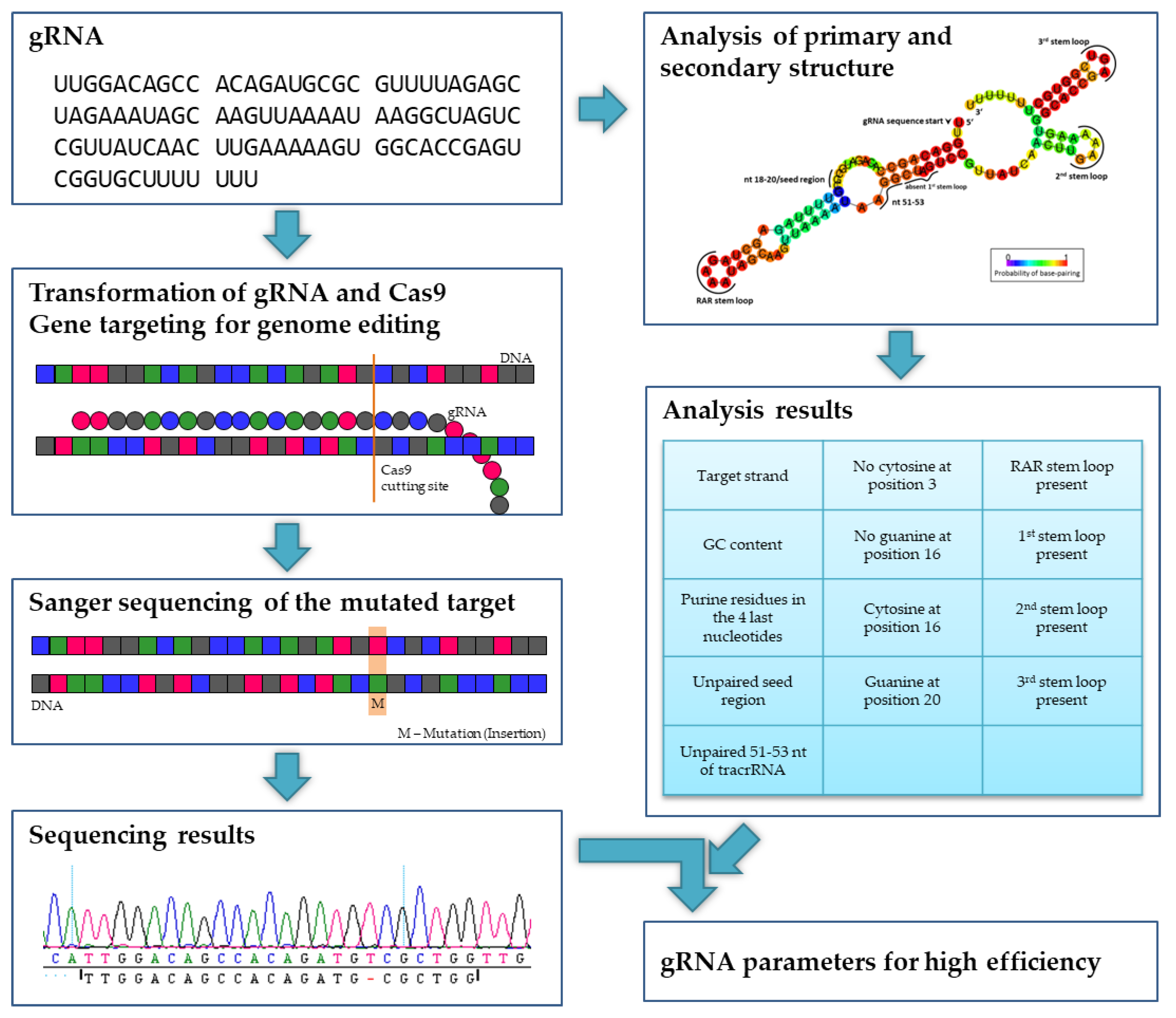



Ijms Free Full Text Evaluating The Efficiency Of Grnas In Crispr Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing In Poplars Html



Protospacer Adjacent Motif Pam Distal Sequences Engage Crispr Cas9 Dna Target Cleavage



2
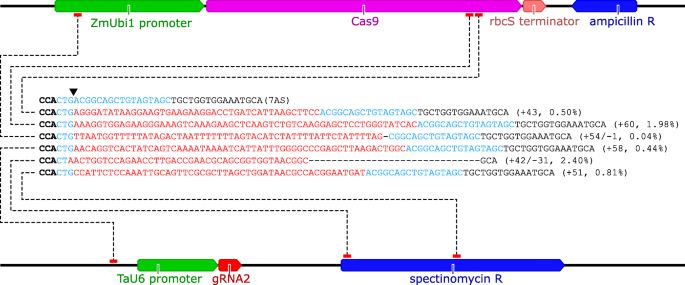



Grna Validation For Wheat Genome Editing With The Crispr Cas9 System Bmc Biotechnology Full Text




Crispr Plant
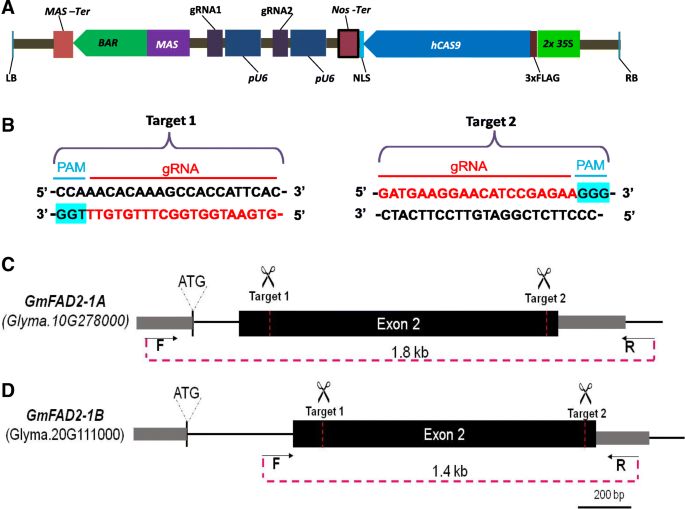



Demonstration Of Highly Efficient Dual Grna Crispr Cas9 Editing Of The Homeologous Gmfad2 1a And Gmfad2 1b Genes To Yield A High Oleic Low Linoleic And A Linolenic Acid Phenotype In Soybean Bmc Plant Biology




Addgene Crispr Guide
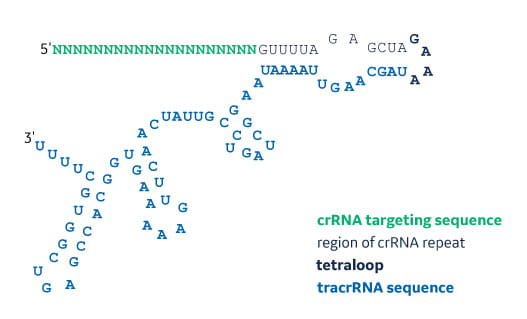



Synthetic Sgrna For Crispr Cas9 Experiments




Binding Of Central Seed Region In Grna Crucial For Cas13 Mediated Download Scientific Diagram




Crispr Cas13d Mediated Efficient Kdm5b Mrna Knockdown In Porcine Somatic Cells And Parthenogenetic Embryos In Reproduction Volume 162 Issue 2 21
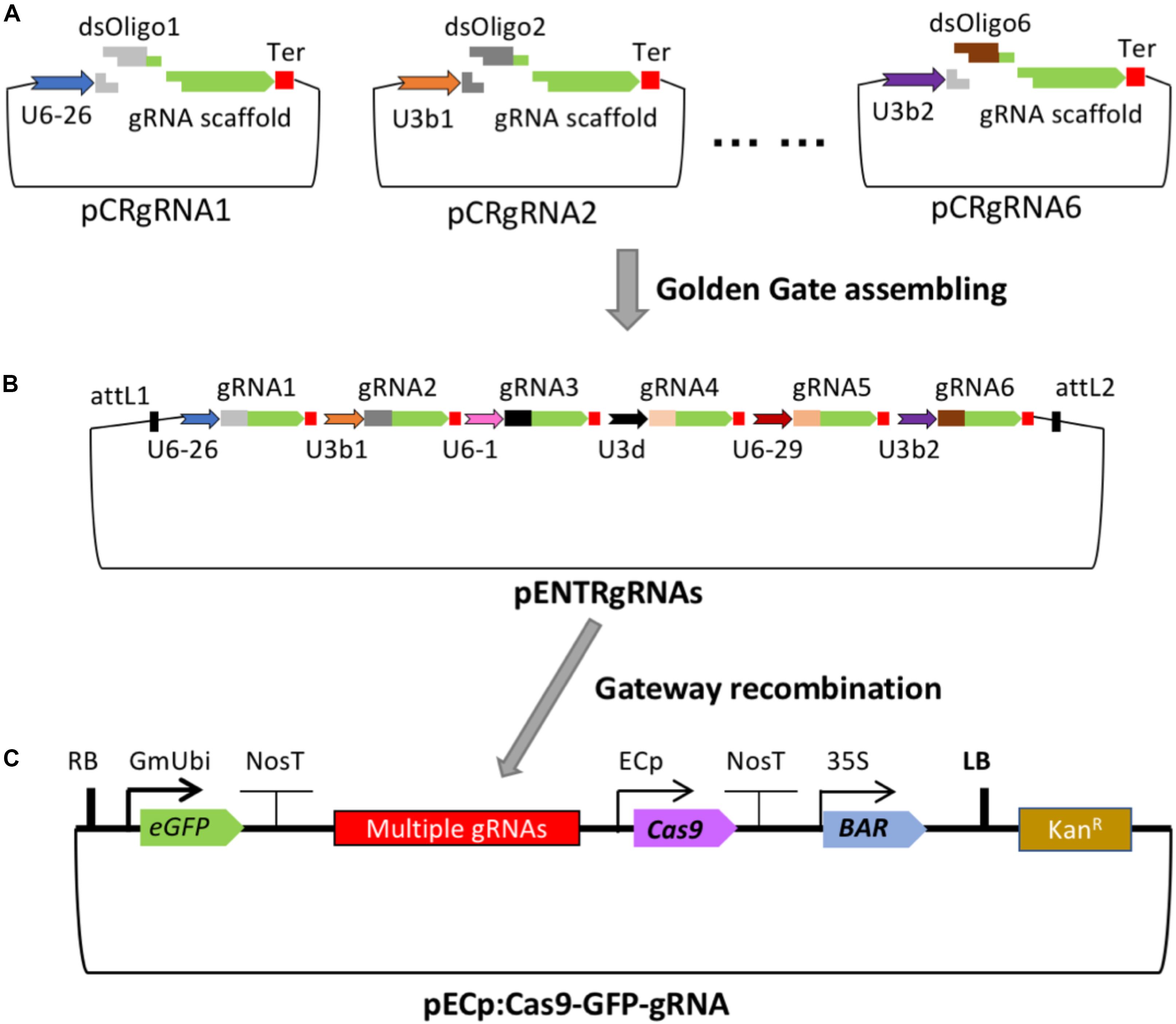



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Based Gene Editing Using Egg Cell Specific Promoters In Arabidopsis And Soybean Plant Science
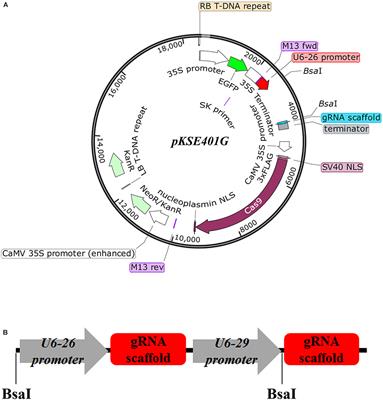



Frontiers Development And Validation Of An Effective Crispr Cas9 Vector For Efficiently Isolating Positive Transformants And Transgene Free Mutants In A Wide Range Of Plant Species Plant Science
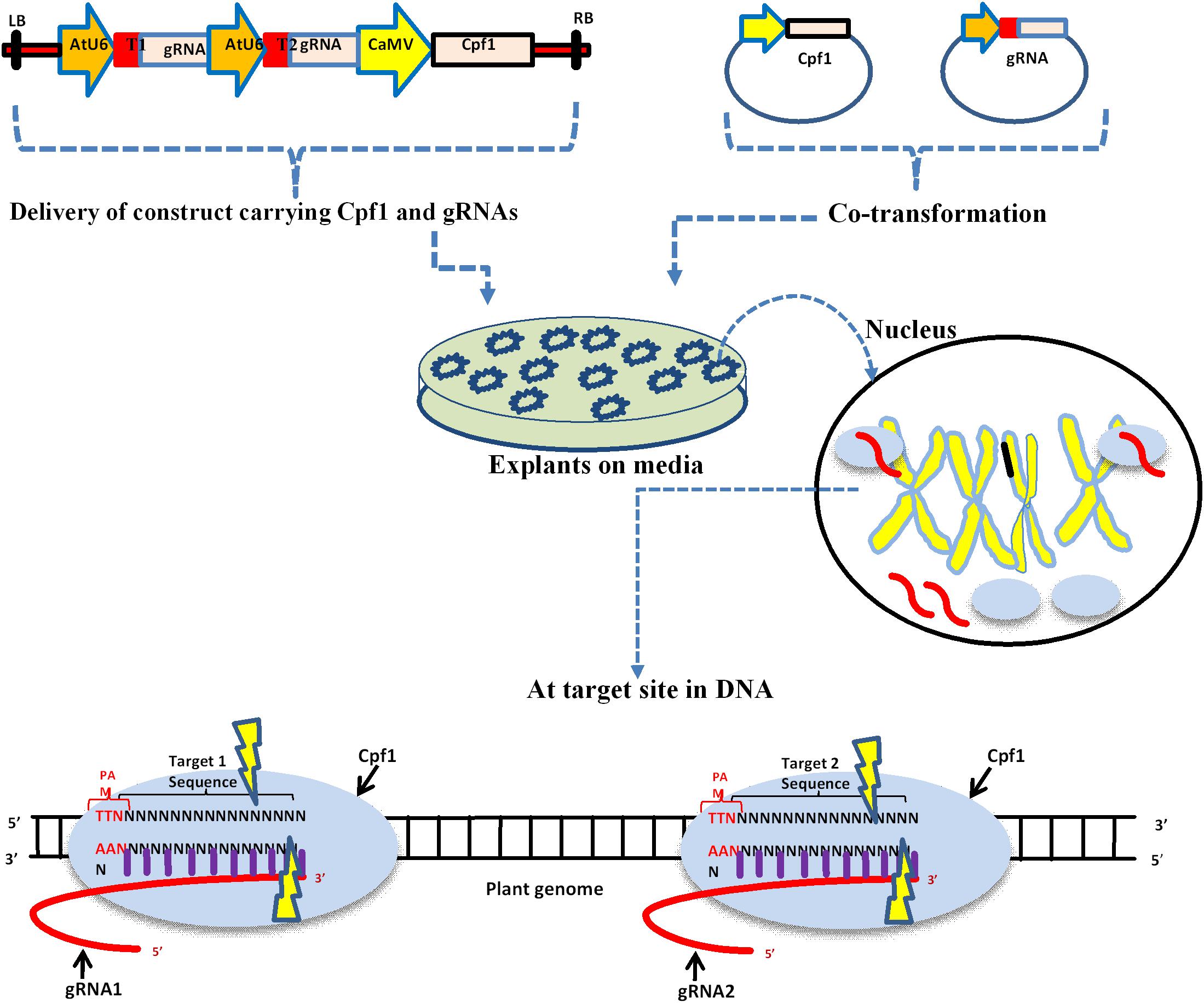



Frontiers The Rise Of The Crispr Cpf1 System For Efficient Genome Editing In Plants Plant Science



Structure Based Design Of Grna For Cas13 Scientific Reports



2



Frontiers Crispr Cas9 Genome Editing Technology A Valuable Tool For Understanding Plant Cell Wall Biosynthesis And Function Plant Science




Schematic Illustration Of Cas9 Grna Genome Editing A Sgrna Mediated Download Scientific Diagram




Addgene Crispr Guide



1




Binding Of Central Seed Region In Grna Crucial For Cas13 Mediated Download Scientific Diagram



Allele Specific Genome Targeting In The Development Of Precision Medicine




Crispr Cas9 Abm Inc




Generating Crispr Cas9 Mediated Monoallelic Deletions To Study Enhancer Function In Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Protocol



Frontiers A Crispr Cas9 Based Mutagenesis Protocol For Brachypodium Distachyon And Its Allopolyploid Relative Brachypodium Hybridum Plant Science
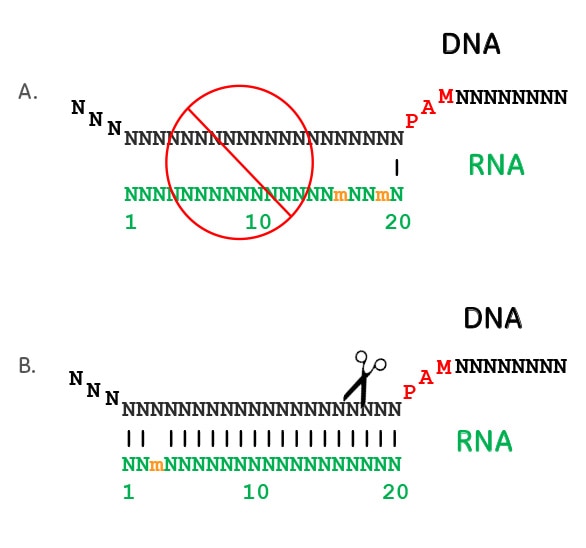



Crispr Cas9 Guide Rna Specificity



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿