Small mastoids = 10 cm Those patients with a predisposing focus of infection in the Nose and PNS were subjected to septal correction and endoscopicDURING the past 17 years, I have treated 41 cases of mastoiditis with Xrays Of these, 16 acute cases were seen in children Of the adults, 15 were acute, seven subacute, and three chronic The chief complaints in all were pain, tenderness to pressure over the mastoidDosto aj app dekhenge ki mastoid ka stenvers view ko kaoise kiya ja sakta hai/ dosto aj k is developed samai main st
Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177
X ray mastoid laws view
X ray mastoid laws view-Infant skull xray lateral view this is an xray image of the skull of an infant taken from a lateral view showing the skull from the side showing 1 frontal bone 2 parietal bones 3 occipital bone 4 lambdoid suture 5 ocular sockets 6 vertex 7 temporal bone 8 mastoid air cells 9 the manSee also Stenvers view;



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key
• mastoid antrum • mastoid air cells • superimposed internal and external acoustic meatuses • mandibular condyle • mastoid process • softtissues 73 petromastoid portion stenvers view • axiolateral oblique posterior profile • prone position, or seatedXray analysis of mastoiditis Radiography of the temporal bone in Cullera is the most appropriate method of roentgenologic examination of its mastoid part Xray detection of bone destructive changes in the initial phase of mastoiditis requires high technical quality radiographs To simplify complex equipment of pictures of the temporal boneThe Xray film of the mastoid taken in the lateral oblique view (Law'sview)wassuperimposedAccordinglythemastoidswere classified as;
The Xray mastoid is done to know mastoid pneumatisation and the level of sinus and dural plates Xray mastoids were obtained by Law's view bilaterally and high resolution computed tomography of the temporal bone was obtained with 1mm cuts in axial and coronal planesInfant skull xray lateral view this is an xray image of the skull of an infant taken from a lateral view showing the skull from the side showing 1 frontal bone 2 parietal bones 3 occipital bone 4 lambdoid suture 5 ocular sockets 6 vertex 7 temporal bone 8 mastoid air cells 9 the man * Radiological investigations included Xray mastoid (Law's lateral oblique view) & HRCT scan of temporal bone both axial and coronal cut for detailed anatomical evaluation of eustachian tube patency and aditus patency * All the cases were initially managed conservatively by aural toileting, antibiotics, antihistaminic and decongestants in
X Ray Mastoid Laws view 2nd Most common X Ray Mastoid X Ray Mastoid Townes view CT & MRI In Menieres disease & Acoustic neuroma Biochemical investigations Haematological Hb%, TLC, DLC RFT BlUrea, Sr Creatinine SrElectrolytes Na, K, Cl, Coagulation Profile BT, CT, PT, APTT, INR RBS Culture and Sensitivity of the ear–Chest XRay special views eg Bucky/Decub –XRay ribs/chest unilateral 3 view –XRay ribs/chest bilateral 4 view 711 –XRay sternum 3 view 710 –XRay entire spine AP/LAT 7 –XRay spine 1 view 740 –XRay neck spine 2 or 3 viewRadiation (Xray) Machine Registration & Compliance The Radiologic Health Branch (RHB) issues State certificates to medical facilities to perform mammography, registers facilities possessing radiation sources such as Xray machines, and notifies the regulated community of radiation control changes The RHB also issues therapy survey and calibration physicist authorizations



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177



Www Ajronline Org Doi Pdf 10 2214 Ajr 97 3 597
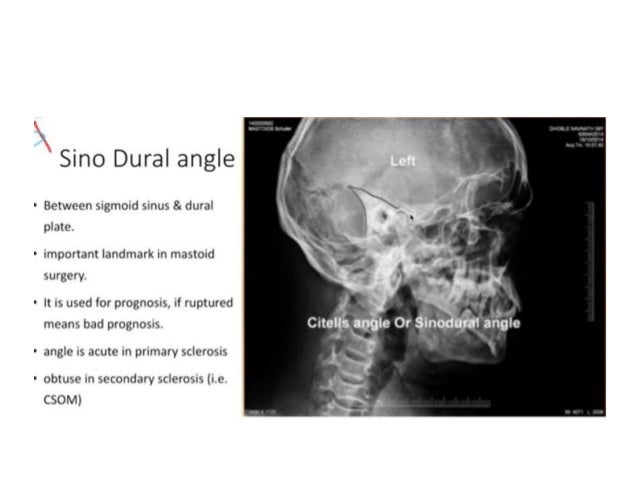
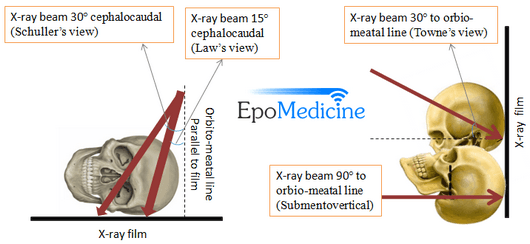
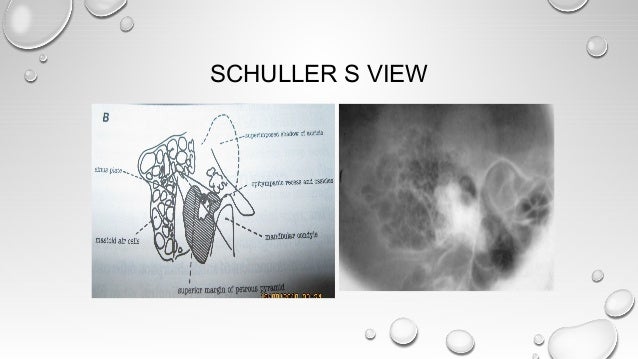
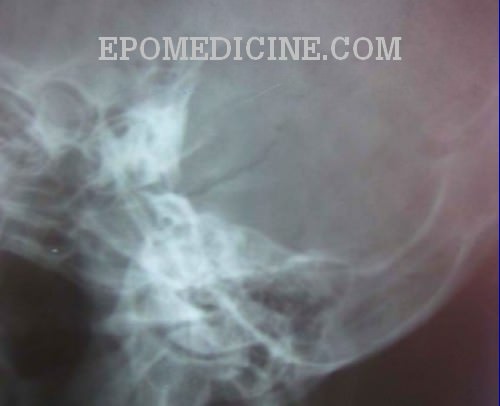
The minimum dose required to produce a progressive cataract is 2 Gy in a single exposure 4 If the lens is in the direct xray beam, the dose to the lens from CT of the temporal bone is in the range of 003 to 006 Gy, but it could be as high as 013 GySchuller's view is a lateral radiographic view of skull principally used for viewing mastoid cells The central beam of Xrays passes from one side of the head and is at angle of 25° caudad to radiographic plate This angulation prevents overlap of images of two mastoid bones Radiograph for each mastoid is taken separatelyView this xray 1 Name the view 2 Write down the differential diagnosis Xray both mastoids Laws view (lateral oblique) Differential diagnosis 1 Large antral cell This is usually bilateral 2 Cholesteatomatous cavity Radiologically this cavity will be surrounded by a rim of sclerosis 3 Operated cavity Pt will give h/o mastoid surgery




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Comparative Medical Radiography Practice And Validation Sciencedirect
A XRay in Los Angeles costs $2,319 on average when you take the median of the 158 medical providers who perform XRay procedures in Los Angeles, CA The least expensive XRay in Los Angeles is $50 for a Finger XRay while the most expensive XRay list price is $12,300 for a XRay of Blood Vessel (Angiography)Chest Xray (Each Oblique View) Orbit XChest Xray (Apicolordotic View) Neck Xray;



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255




Pps Radiology
A plain Xray of mastoid/Law's view was done to assess the position of dural and sinus plates Routine haematological and biochemistry investigations were done to assess fitness for anaesthesia After the examination and appropriate investigations informed consent was taken for participation in the trialView and Download PowerPoint Presentations on X Ray Mastoid PPT Find PowerPoint Presentations and Slides using the power of XPowerPointcom, find free presentations research about X Ray Mastoid PPT About 13 results (177 seconds) Laws view mastoids positioning" Keyword Found Websites Keywordsuggesttoolcom DA 28 PA 39 MOZ Rank 69 Schuller's view is a lateral radiographic view of skull principally used for viewing mastoid cellsThe central beam of Xrays passes from one side of the head and is at angle of 25° caudad to radiographic plate



Radiology Case Schuller View Antrotomy



New Microsoft Office Power Point Presentation
Examination of the mastoid can be made possible with the AP view which is also called posteroanterior and anteroposterior The Xray beam is directed either postero anteriorly or antero posteriorly along the orbitomeatal line at an angle of 90 degrees to the film Price for XRay Mastoid (Right) (AP View) TestVersion 269 XR Mastoid bilateral Law and Mayer and Stenver and TowneActive FullySpecified Name Component Views Law Mayer Stenver Towne Property Find Time Pt System Head>Mastoidbilateral Scale Doc Method XR Additional Names Short Name XR MastoidBl LawMayerStenverTowne Associated Observations This panel contains the recommended The size of the mastoids was measured by using a graph paper, on which the Xray film of the mastoid taken in the lateral oblique view (Law's view) was superimposed Patients with CSOM (TTD) with less than 3 months of dry ear and small size mastoids on Xray were subjected to cortical mastoidectomy and type I tympanoplasty;




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Mastoids Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
View and Download PowerPoint Presentations on Steam Inhalation PPT Find PowerPoint Presentations and Slides using the power of XPowerPointcom, find free presentations research about Steam Inhalation PPTCentral Ray The horizontal central ray is centered in the midline of the occiput so that the emergent ray exits the patient in the midline at the level of the anterior nasal spine at the upper border of the maxilla Various views for mastoid • LAW's view lateral Oblique viewThe xray oblique view test gives much useful information regarding the mastoids It provides results about the pathology of the mastoids in the following manner Distinguishing whether the mastoids are cellular or acellular Determining the width of the cortical bone Projecting the symmetry of both the mastoids




Mastoid Series Normal Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org




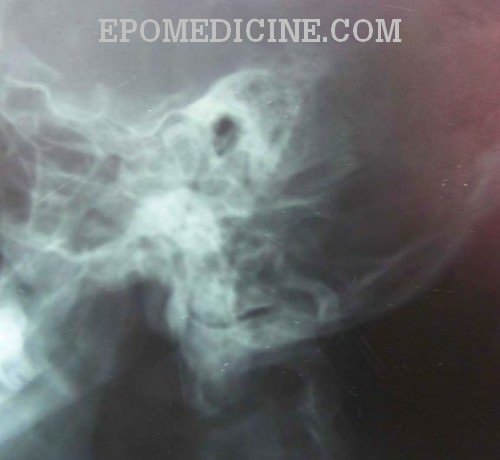
Digital X Ray Of Mastoid Region Law S Lateral Oblique View Showing Download Scientific Diagram
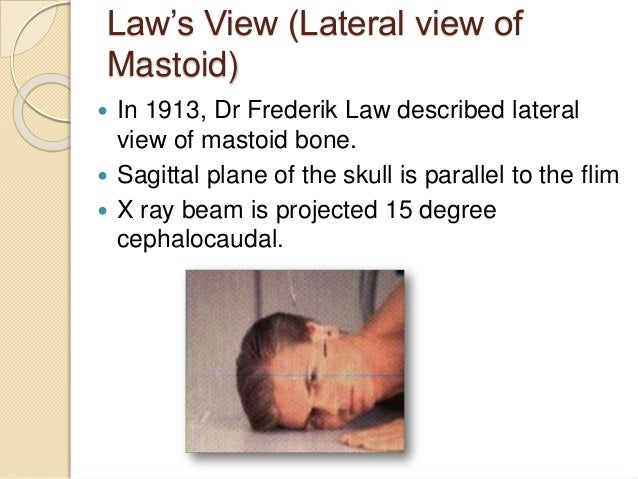
Types of Mastoid XRay 15 degree lateral oblique(Law) 30 degree lateral oblique(Schuller) commonly done 45 degree lateral oblique(Myer Owen) Advantage of schuller & owen Better visualisation of key areas of mastoid(attic, aditus, antrum) Towne's view b/l AP view showing both mastoids & IACXray mastoids were obtained by Law's view bilaterally and high resolution computed tomography of the temporal bone was obtained with 1mm cuts in axial and coronal planes Purpose of the study to compare regarding the pneumatisation in chronic suppurative otitis media with xray both mastoids and HRCT temporal bone IOML is perpendicular to front edge of cassette Rotate head from lateral position (face down towards bucky or cassette by 15°) midsagittal plane of the head is rotated 15° from flat surface or plane of cassette Angle central ray 15° caudad centered to 4 cm superior to upside EAM (to pass through downside TMJ)




X Rays In Ent



Q Tbn And9gctj3zr Hrj2dnckcxuveb Enkdddksnlfto1uq1smrpcw7sbym2 Usqp Cau
In a good quality xray, it avoids overlap of impressions of both mastoid bones;Schüller's view (Runstrom) is a lateral view of the mastoid obtained with the sagittal plane of the skull parallel to the film and with a 30° cephalocaudal angulation of the xray beam These 30° in Schüller's view displaces the arcuate eminence of the petrous bone downward and shows the antrum and the upper part of the atticPurpose and Structures Shown An additional view to evaluate the mandible Position of patient Lying on the side (left or right) with a vertical beam angled at 15 degrees Position of part Remove dentures, facial jewelry, earrings, and anything from the hair The Xray




Stenvers View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine
An xray mastoids lateral oblique view (Laws) showed (L) mastoid to be sclerotic with evidence of bone destruction CORRELATION OF RADIOLOGICAL AND OPERATIVE FINDING REGARDING THE CELLULARITY OF MASTOID IN CHRONIC SUPPURATIVE OTITIS MEDIA (ATTICOANTRAL DISEASE)Hello!!!!what's up guys, kaise ho dosto?It is an alternative x ray to the Law projection where 15 degrees is used;



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255



X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram
Limited License Xray (General Xray Machine Operator ) Can perform under direct supervisor of licensed pratitioner within scope of practitioner's practice The minimum requirement for any individual performing xray procedures in the state of Ohio is that the individual be licensed as a general xray machine operator6 An xray mastoids lateral oblique view (Laws) showed (L) mastoid to be sclerotic with evidence of bone destruction 6 Sethi et al evaluated the influence of presence and duration of chronicMastoids XRay is usually ordered by doctors if you have these indications Fever,



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine




Cochlear Implant Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Mastoid process (Processus mastoideus) The skull is composed of multiple small bones held together by fibrous joints Its inferior surface gives rise to a number of projections, and these allow for the attachment of many structures of the neck and faceThe temporal bone is one of the bones of the skull before thinsection highresolution CT, many Xray views and modifications were used Today, only few views are used STENVERS VIEW – oblique projection (angled 45° forward) to provide unobstructed view of petrous bone, bony labyrinth, internal auditory canal SCHÜLLER VIEW – along ear canal – demonstrates mastoid air cellsMastoid Xray (Laws & Mayers) Chest Bucky (Ap) Mastoiditis;



Www Thieme Connect De Products Ebooks Pdf 10 1055 B 0034 619 Pdf



Q Tbn And9gcr Gqzw Khiynlryxbmvranbxtqbocewfdixhn H7gnmj4smjf Usqp Cau
Abstract T he x ray study of the mastoid region, which was begun in March, 1908, has undergone a slow but gratifying metamorphosis Undertaken with grave doubts as its practical value, it has developed into a method which rivals in its accuracy other recognized methods of physical examination At the inception of the work, it promised at best to show the anatomy and the grosser chronic changes in the mastoidVIEWS LAW MAYER STENVER TOWNE First major axiscomponent or analyte Property FIND Second major axisproperty observed (eg, mass vs substance) Time Aspect PT Third major axistiming of the measurement (eg, point in time vs 24 hours) System HEAD>MASTOIDBILATERALThe mastoid cells' ' This well expresses the old view regarding the sclerosed mastoid frequently found at opera tion Cheatle has more recently stated that in infancy, with the exception of the mastoid antrum and a few cells on its outer wall, the mastoid consists of diplo?tic structure further, that this socalled infantile type persists in



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255



1
Trauma, surgical hardware Xray first CT for preoperative planning of fractures CT for occult fracture in younger patients MR for occult fracture in older patients CT arthrography without and with contrast for arthroplasty complications Masses Xray first for bony lesions Ultrasound for suspected lipoma Otherwise MRI without and withMastoids XRay may be performed to assess damage to the ear as well as the source of pain and discomfort to the area There are multiple XRay views when checking your mastoids Who should get this test? Lateral, oblique, anteroposterior, and semiaxial views and modifications of these views were produced by angulation of the xray beam or the patient's head The lateral mastoid view ( Fig 381 ) is the only projection still used in some imaging centers, largely to confirm a diagnosis of acute mastoiditis or substantiate previous mastoid disease



Www Jemds Com Latest Articles Php At Id 7457




Ce4rt X Ray Positioning Of The Mastoid Process For Radiologic Techs
Nasal Bone – apl (Water's View And Soft Tissue Lat) Chest Xray (Ap, Lat Below 5 Yrs Old) Nasal Bone Soft Tissue Lat;During imaging, separate xrays of both mastoid bones is taken;CT has typically overtaken xray as the modality of choice for imaging of the mastoid This is a normal mastoid series for reference 1 article features images from this case




60 Radiographs Labeling Ideas Radiography Radiology Technologist Radiology




Skull Towne View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
We have been studying how to make xray examination of the temporal bone, middle ear, and mastoid process as simple and informative as possible What is required of us by the otologic surgeon is a demonstration of the middle ear and ossicles, the epitympanic space, bony bridge, aditus, and the mastoid antrum



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




How To Do Mastoids In X Ray Table Youtube




Nbde Radiology Flashcards Quizlet
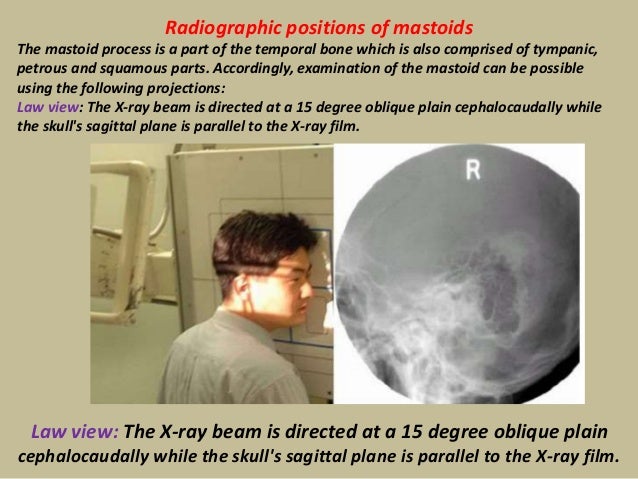



Presentation1 Pptx Radiological Anatomy Of The Petrous Bone
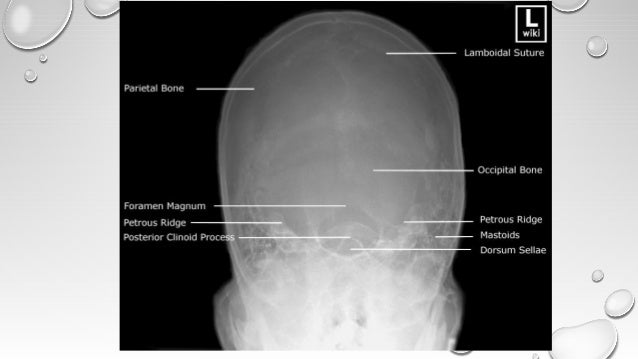



Radiological Imaging In Head And Neck And Relevant Anatomy



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




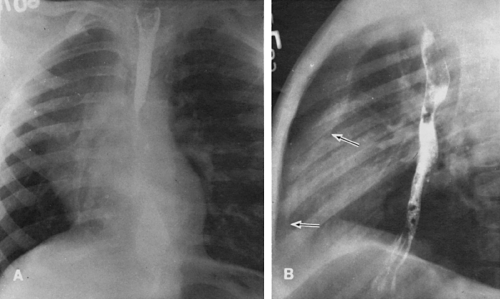
A And B X Rays Both Mastoids Law S View Showing Radio Opaque Foreign Download Scientific Diagram



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key
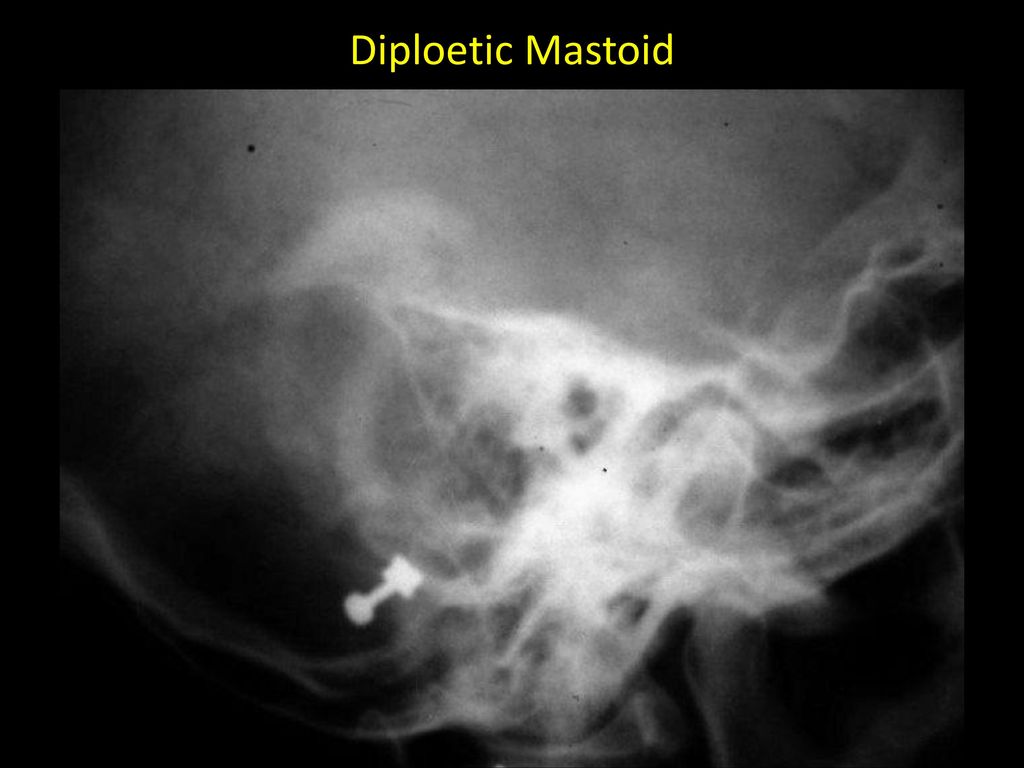



Dr Sujan Chhetri Ms Ent Ppt Video Online Download
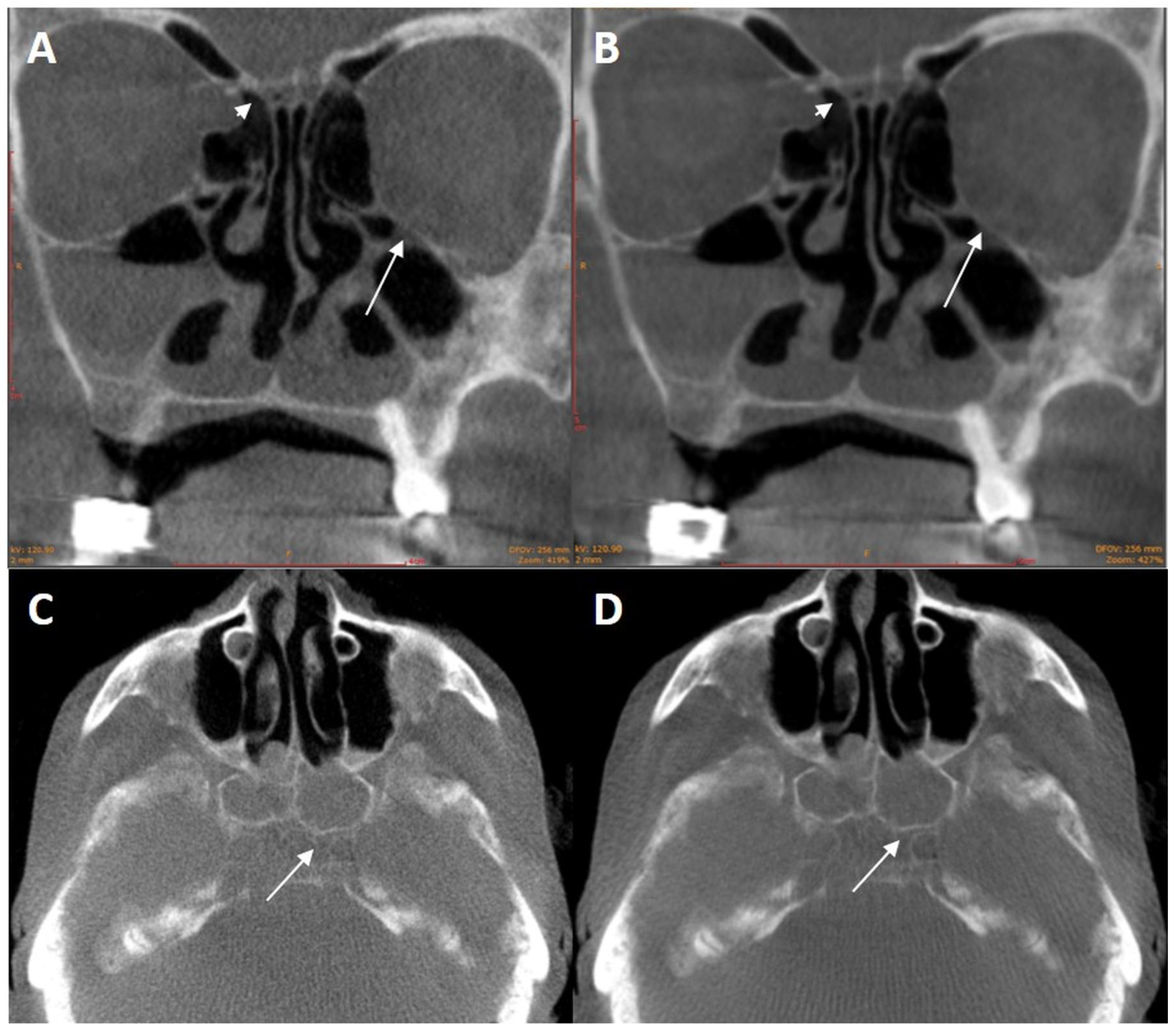



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Cone Beam Ct Imaging Of The Paranasal Region With A Multipurpose X Ray System Image Quality And Radiation Exposure Html



Q Tbn And9gcrvo55xynu9ebeop7emyk3bh41lvbtvulvq 2afm9q Usqp Cau
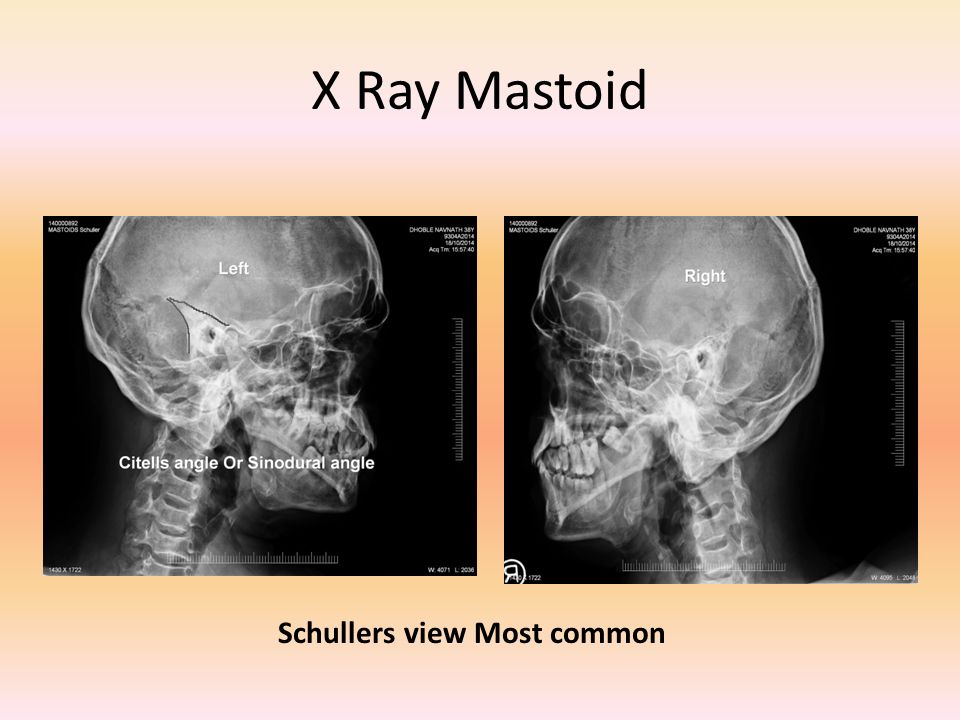



Laws View X Ray 鬼画像無料




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
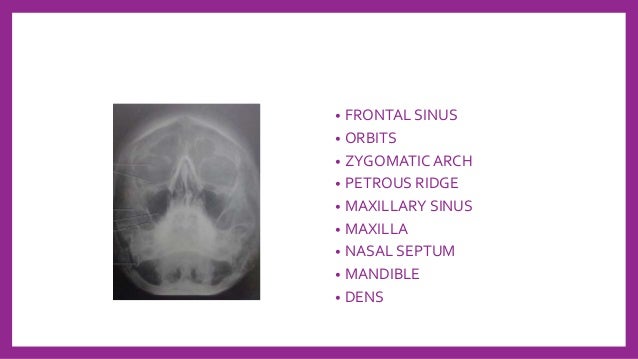



Skull Radiography Techniques And Reporting



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key



Http Www Neurosurgeryresident Net D diagnostics D45 59 neuroimaging X Ray ct mri pet mrs D47 x Ray Pdf
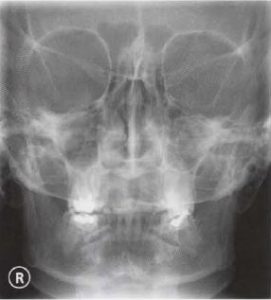



Ce4rt Radiographic Positioning Face And Mandible For X Ray Techs




The Modified Stenver S View For Cochlear Implants What Do The Surgeons Want To Know
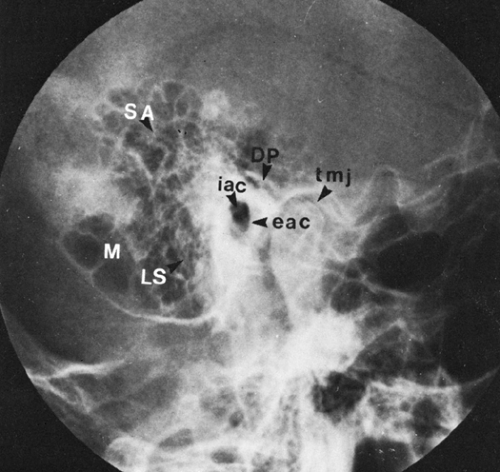



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key
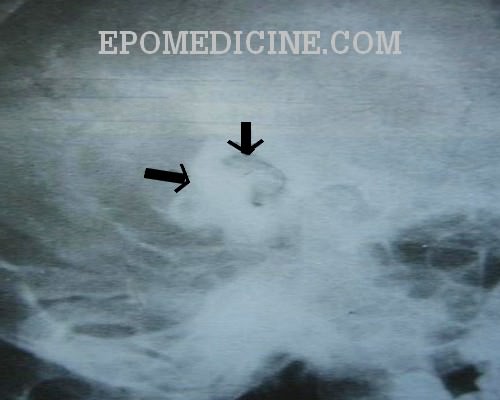



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine




The Temporal Bone Radiology Key




Modified Law Method Tmj Radtechonduty




How To Do Mastoids In X Ray Table Youtube




Mastoids Lat Obl View Anatomy And Physiology Part 23 Youtube
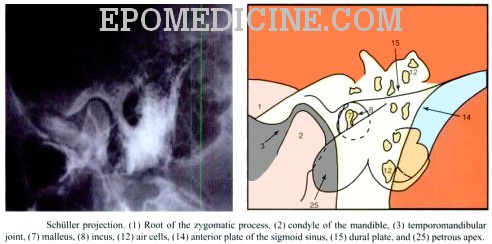



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine




Mastoid Stenvers View Youtube



Radiological Imaging In Head And Neck And Relevant Anatomy



Radiology In Head And Neck By Kanato T Assumi




Mastoids Lat Obl View Anatomy And Physiology Part 23 Youtube




Radiographic Positions Of Mastoids Pdf Human Head And Neck Human Anatomy



Www Jemds Com Latest Articles Php At Id 7457



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12301/chest-x-ray-pa-view_english.jpg)



Radiological Anatomy X Ray Ct Mri Kenhub




Technique Of X Ray Mastoid Towns View Ep 27 Mastoid Towns View Positioning Bangla Tutorial Youtube




X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram




Skull Towne Method Ap Axial Projection Radtechonduty
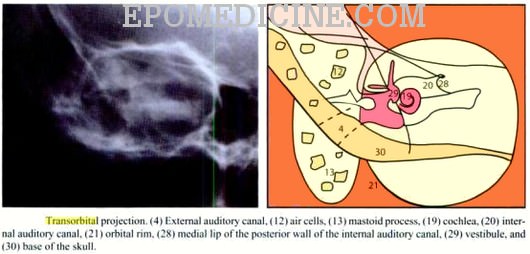



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine



Ce4rt X Ray Positioning Of The Mastoid Process For Radiologic Techs



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Mastoid Series Normal Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




Submentovertex Smv Projection Skull Series Radtechonduty



Http Www Angelfire Com Sk3 Kshemaent Students Ent Radiology A Pdf




The Modified Stenver S View For Cochlear Implants What Do The Surgeons Want To Know



Osce Notes In Otoradiology By Drtbalu Osce Notes In Otolaryngology
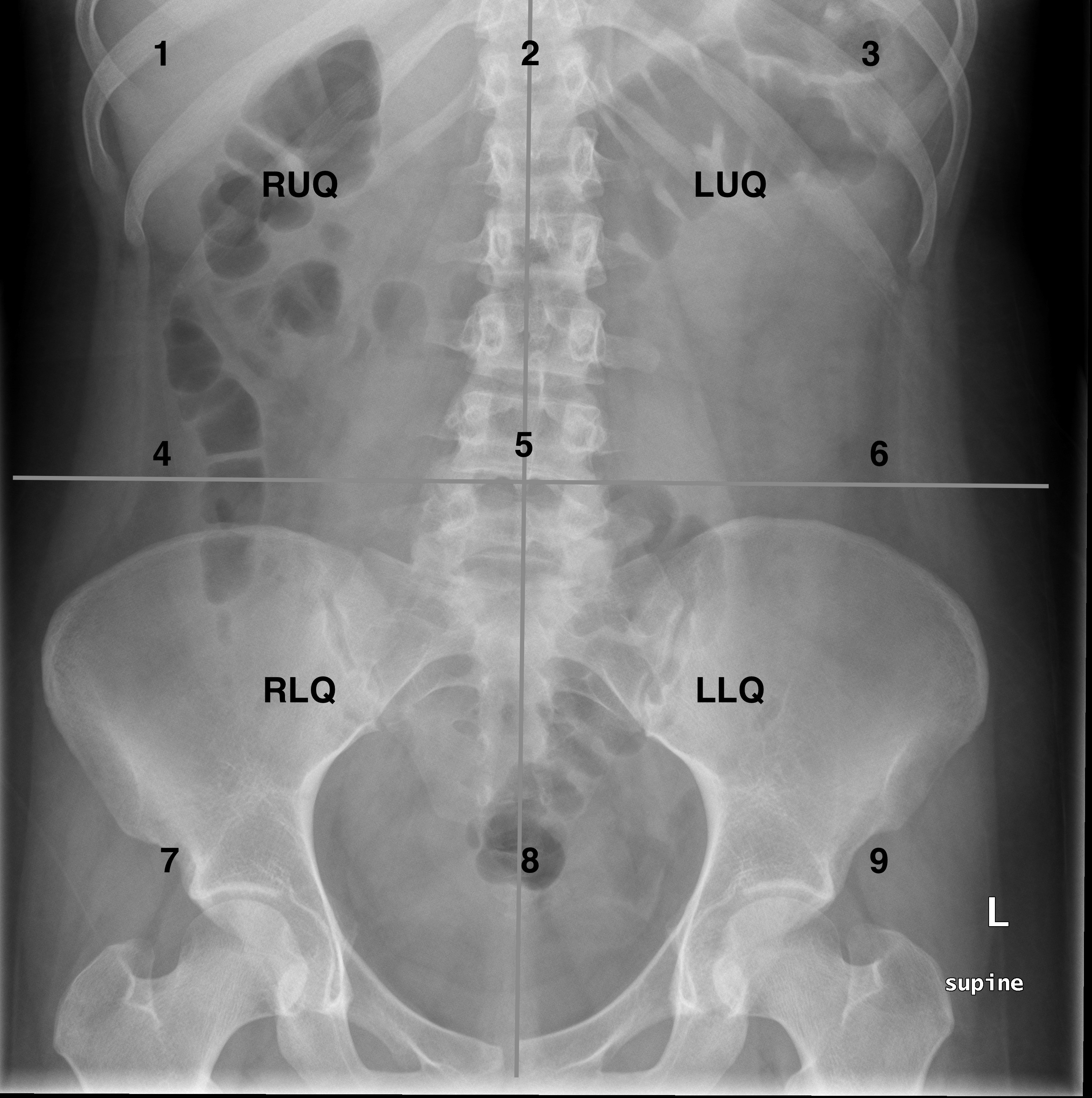



Approach To The Abdominal X Ray Axr Undergraduate Diagnostic Imaging Fundamentals
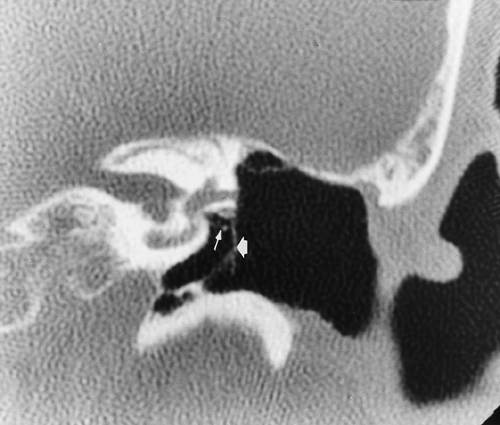



The Temporal Bone Radiology Key



Med Und Edu Radiology Files Docs Xray Film Reading Made Easy Pdf
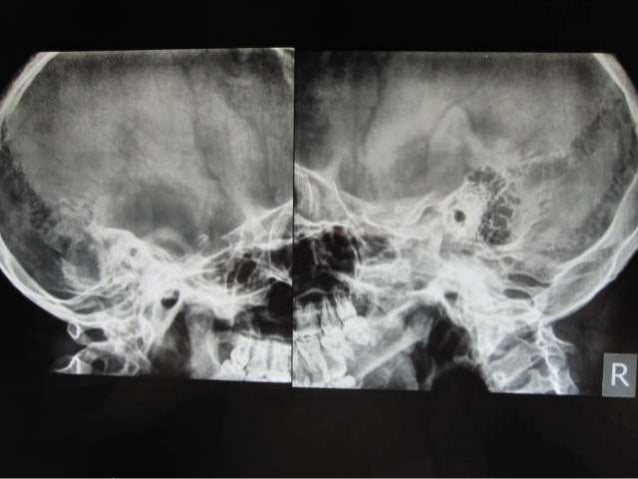



Xrays In Ent Dr Ashly Alexander



Digital X Ray Of Mastoid Region Law S Lateral Oblique View Showing Download Scientific Diagram
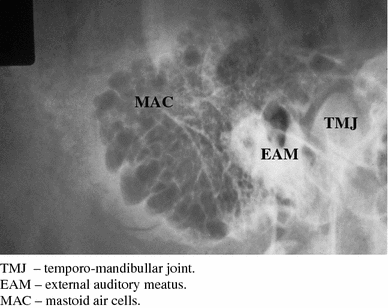



The Growth Rate And Size Of The Mastoid Air Cell System And Mastoid Bone A Review And Reference Springerlink



Ce4rt X Ray Positioning Of The Mastoid Process For Radiologic Techs
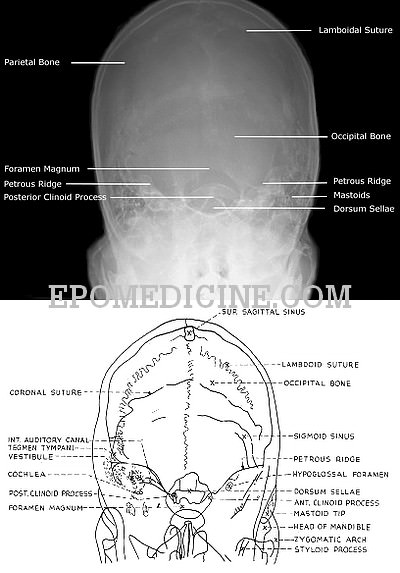



X Ray Of Mastoids Epomedicine



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255




Xrays In Ent Dr Sujan Chhetri Ms Ent




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Waters View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Schuller S View Wikipedia



Top Photos In Infant Skull X Ray Lateral View




Mastoids Radiographic Anatomy Medical Radiography Radiology Imaging Radiology Student



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12296/chest_PA.jpg)



Radiological Anatomy X Ray Ct Mri Kenhub




Digital X Ray Of Mastoid Region Law S Lateral Oblique View Showing Download Scientific Diagram



Pubs Rsna Org Doi Pdf 10 1148 80 2 255



Www Thieme Connect De Products Ebooks Pdf 10 1055 B 0034 619 Pdf
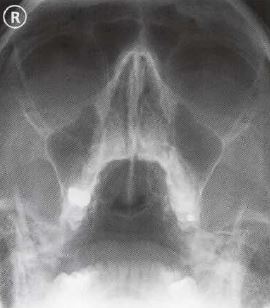



Ce4rt Radiographic Positioning Face And Mandible For X Ray Techs




X Ray Mastoid Lateral Oblique Law S View Left Side Shows Sclerosis Download Scientific Diagram




View Image




Role Of X Rays In Otolaryngolgoy Esophagus Medical Imaging



Nanopdf Com Download File 3159 Pdf



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿